Publications
Electronic versions are provided as a professional courtesy to ensure timely dissemination of academic work for individual, noncommercial purposes. Copyright and all rights therein resides with the respective copyright holders, as stated within each paper. These files may not be reposted without permission.
Blindsight videos related to the publication: de Gelder, B. , Humphrey, N. & Pegna, A. (2024). On the bright side of blindsight. Considerations from new observations of awareness in a blindsight patient
Synopsis of Main Lab Papers
 Here you can find one-page summaries of some of the lab's most significant publications over the years
Here you can find one-page summaries of some of the lab's most significant publications over the years
Submitted
 Kolinsky, R., Franco, A., Leite, I., Ventura, P., de Gelder, B.(2024). Holistic when useful, analytic when required:Literacy promotes flexibility in face processing.[submitted for publication]
Kolinsky, R., Franco, A., Leite, I., Ventura, P., de Gelder, B.(2024). Holistic when useful, analytic when required:Literacy promotes flexibility in face processing.[submitted for publication]
In press
 Georgakopoulou, N., Kosti, M. V., Diplaris, S., Benayoun, M., Camurri, A., de Gelder, B., Wald-Fuhrmann, M., Koulali, P., Valsamidou, K., Bronner, K., Wanner, L., Gaki, F., Vrochidis, S., Kompatsiaris, I. (In press). ReSilence: Retune the Soundscape of future cities through art and science collaboration.
Georgakopoulou, N., Kosti, M. V., Diplaris, S., Benayoun, M., Camurri, A., de Gelder, B., Wald-Fuhrmann, M., Koulali, P., Valsamidou, K., Bronner, K., Wanner, L., Gaki, F., Vrochidis, S., Kompatsiaris, I. (In press). ReSilence: Retune the Soundscape of future cities through art and science collaboration.
Preprints
 Danesin, L., de Gelder, B., van den Stock, J. (2023). Facial emotion recognition in patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: an exploratory study
Danesin, L., de Gelder, B., van den Stock, J. (2023). Facial emotion recognition in patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: an exploratory study
 Kupers, R., Zhan, M., Pare, S., Dricot, L., Vaessen, M., & de Gelder, B. (2022). Brain morphometric changes in congenitally blind subjects: a 7 Tesla MRI study. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.18.492367
Kupers, R., Zhan, M., Pare, S., Dricot, L., Vaessen, M., & de Gelder, B. (2022). Brain morphometric changes in congenitally blind subjects: a 7 Tesla MRI study. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.18.492367
 Tanaka, A., Takagi, S., Harada, T., Huis, E., de Gelder, B., Hamano, Y., ... & Sadato, N. (2020). Culture influences audiovisual emotion perception in early sensory areas. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.10.332437
Tanaka, A., Takagi, S., Harada, T., Huis, E., de Gelder, B., Hamano, Y., ... & Sadato, N. (2020). Culture influences audiovisual emotion perception in early sensory areas. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.10.332437
 Zhan, M., Goebel, R., & de Gelder, B. (2021). Subjective understanding of actions and emotions involves the interplay of the semantic and action observation networks in the brain. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.15.439961
Zhan, M., Goebel, R., & de Gelder, B. (2021). Subjective understanding of actions and emotions involves the interplay of the semantic and action observation networks in the brain. BioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.15.439961
2025
 Marrazzo G, De Martino F, Mukovskiy A, Giese MA, de Gelder B (2025) Neural encoding of biomechanically (im)possible human movements in occipitotemporal cortex. PLoS Comput Biol 21(12): e1013694. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1013694
Marrazzo G, De Martino F, Mukovskiy A, Giese MA, de Gelder B (2025) Neural encoding of biomechanically (im)possible human movements in occipitotemporal cortex. PLoS Comput Biol 21(12): e1013694. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1013694
 Li, B., Marrazzo, G., Poyo Solanas, M. et al. Distinct information flows for different whole-body actions across LOTC subdivisions. Commun Biol 9, 74 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-025-09339-3
Li, B., Marrazzo, G., Poyo Solanas, M. et al. Distinct information flows for different whole-body actions across LOTC subdivisions. Commun Biol 9, 74 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-025-09339-3
 Klincewicz M, Cheng T, Schmitz M, Sebastián MÁ, Snyder JS. What makes a theory of consciousness unscientific? Nat Neurosci. 2025 Apr;28(4):689-693. doi: 10.1038/s41593-025-01881-x.
Klincewicz M, Cheng T, Schmitz M, Sebastián MÁ, Snyder JS. What makes a theory of consciousness unscientific? Nat Neurosci. 2025 Apr;28(4):689-693. doi: 10.1038/s41593-025-01881-x.
 Van Hove LI, De Winter FL, Zhu Q, Cypers G, Vanduffel W, de Gelder B, Vandenbulcke M, Van den Stock J. (2025) Converging cross-modal evidence for a phylogenetic age effect in neurodegenerative susceptibility. Brain. 2025 May 13;148(5):e34-e36. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaf050.
Van Hove LI, De Winter FL, Zhu Q, Cypers G, Vanduffel W, de Gelder B, Vandenbulcke M, Van den Stock J. (2025) Converging cross-modal evidence for a phylogenetic age effect in neurodegenerative susceptibility. Brain. 2025 May 13;148(5):e34-e36. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaf050.
 Lu J, Riecke L, Ryan BE, de Gelder B. (2025). The contribution of body perception to self-identity: an event-related potential study. (2025) Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2025 Mar 10;20(1):nsaf020. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaf020.
Lu J, Riecke L, Ryan BE, de Gelder B. (2025). The contribution of body perception to self-identity: an event-related potential study. (2025) Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2025 Mar 10;20(1):nsaf020. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaf020.
 Smekal V, Hecquard J, Kuhne S, Occidental N, Lecuyer A, Mace M, de Gelder B. Influence of Haptic Feedback on Perception of Threat and Peripersonal Space in Social VR. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2025 May;31(5):2986-2994. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2025.3549884. Epub 2025 Apr 25.
Smekal V, Hecquard J, Kuhne S, Occidental N, Lecuyer A, Mace M, de Gelder B. Influence of Haptic Feedback on Perception of Threat and Peripersonal Space in Social VR. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2025 May;31(5):2986-2994. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2025.3549884. Epub 2025 Apr 25.
 Smekal V, Poyo Solanas M, de Gelder B. Disentangling dynamic information and temporal order processing of human action perception. PNAS Nexus. 2025 Mar 24;4(3):pgaf067. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf067. eCollection 2025 Mar.
Smekal V, Poyo Solanas M, de Gelder B. Disentangling dynamic information and temporal order processing of human action perception. PNAS Nexus. 2025 Mar 24;4(3):pgaf067. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf067. eCollection 2025 Mar.
 Mejía MA, Valdés-Sosa M, de Gelder B, Bobes MA. (2025) Disconnection between parietal and temporal areas without simultanagnosia: a case study of prosopagnosia. Neurocase. 2025 Aug;31(3):124-132. doi: 10.1080/13554794.2025.2489929. Epub 2025 Apr 12
Mejía MA, Valdés-Sosa M, de Gelder B, Bobes MA. (2025) Disconnection between parietal and temporal areas without simultanagnosia: a case study of prosopagnosia. Neurocase. 2025 Aug;31(3):124-132. doi: 10.1080/13554794.2025.2489929. Epub 2025 Apr 12
 Villa MC, Borriero A, Diano M, Ciorli T, Celeghin A, de Gelder B, Tamietto M. (2025). Dissociable neural networks for processing fearful bodily expressions at different spatial frequencies. Cereb Cortex. 2025 Apr 1;35(4):bhaf067. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaf067.
Villa MC, Borriero A, Diano M, Ciorli T, Celeghin A, de Gelder B, Tamietto M. (2025). Dissociable neural networks for processing fearful bodily expressions at different spatial frequencies. Cereb Cortex. 2025 Apr 1;35(4):bhaf067. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaf067.
 Lu J, Riecke L, de Gelder B. Behavioral and neural evidence for perceptual predictions in social interactions. (2025) Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025 Jun 11;3:IMAG.a.38. doi: 10.1162/IMAG.a.38. eCollection 2025
Lu J, Riecke L, de Gelder B. Behavioral and neural evidence for perceptual predictions in social interactions. (2025) Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025 Jun 11;3:IMAG.a.38. doi: 10.1162/IMAG.a.38. eCollection 2025
 Moses E, Scambler J, Taubert J, Lo AHY, Thompson K, de Gelder B, Pegna AJ. (2025) Temporal Lobectomy Evidence for the Role of the Amygdala in Early Emotional Face and Body Processing. eNeuro. 2025 Feb 14;12(2):ENEURO.0114-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0114-24.2024. Print 2025 Feb.
Moses E, Scambler J, Taubert J, Lo AHY, Thompson K, de Gelder B, Pegna AJ. (2025) Temporal Lobectomy Evidence for the Role of the Amygdala in Early Emotional Face and Body Processing. eNeuro. 2025 Feb 14;12(2):ENEURO.0114-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0114-24.2024. Print 2025 Feb.
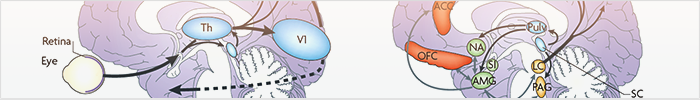
 de Gelder B, Humphrey N, Pegna AJ. (2025) On the bright side of blindsight. Considerations from new observations of awareness in a blindsight patient. Cereb Cortex. 2025 Jan 8;35(1):42-48. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae456. PMID: 39604004 Free PMC article.
de Gelder B, Humphrey N, Pegna AJ. (2025) On the bright side of blindsight. Considerations from new observations of awareness in a blindsight patient. Cereb Cortex. 2025 Jan 8;35(1):42-48. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae456. PMID: 39604004 Free PMC article.
Chapter
 Poyo Solanas, M., de Gelder, B., 2025. Social interaction—Recent behavioral and brain studies. In: Grafman, J.H. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of the Human Brain, Second Edition, vol. 4, pp. 410–421. USA: Elsevier. ISBN: 9780128204801
Poyo Solanas, M., de Gelder, B., 2025. Social interaction—Recent behavioral and brain studies. In: Grafman, J.H. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of the Human Brain, Second Edition, vol. 4, pp. 410–421. USA: Elsevier. ISBN: 9780128204801
2024
 de Gelder, B. , Humphrey, N. & Pegna, A. (2024). On the bright side of blindsight. Considerations from new observations of awareness in a blindsight patient
de Gelder, B. , Humphrey, N. & Pegna, A. (2024). On the bright side of blindsight. Considerations from new observations of awareness in a blindsight patient
 Abassi, E., Bognár, A., de Gelder, B., Giese, M., Isik, L., Lappe, A., ... & Vogels, R. (2024). Neural Encoding of Bodies for Primate Social Perception. Journal of Neuroscience, 44(40).
Abassi, E., Bognár, A., de Gelder, B., Giese, M., Isik, L., Lappe, A., ... & Vogels, R. (2024). Neural Encoding of Bodies for Primate Social Perception. Journal of Neuroscience, 44(40).
 Poyo Solanas, M., Zhan, M., & de Gelder, B. (2024). Ultrahigh field fMRI reveals different roles of temporal and fronto-parietal cortices in subjective awareness. Journal of Neuroscience, e0425232023. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0425-23.2023
Poyo Solanas, M., Zhan, M., & de Gelder, B. (2024). Ultrahigh field fMRI reveals different roles of temporal and fronto-parietal cortices in subjective awareness. Journal of Neuroscience, e0425232023. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0425-23.2023
 Chesley, J., Riecke, L., Lu, J., Vogels, R., & de Gelder, B. (2024). Theta activity discriminates high-level, species-specific body processes. Imaging Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1162/imag_a_00150
Chesley, J., Riecke, L., Lu, J., Vogels, R., & de Gelder, B. (2024). Theta activity discriminates high-level, species-specific body processes. Imaging Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1162/imag_a_00150
 Smekal, V., Poyo Solanas, M., Fraats, E. I. C., & de Gelder, B. (2024). Differential contributions of body form, motion, and temporal information to subjective action understanding in naturalistic stimuli. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2024.1302960
Smekal, V., Poyo Solanas, M., Fraats, E. I. C., & de Gelder, B. (2024). Differential contributions of body form, motion, and temporal information to subjective action understanding in naturalistic stimuli. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2024.1302960
 Christensen, A., Taubert, N., Veld, E. M. J. H. I. ’., de Gelder, B., & Giese, M. A. (2024). Perceptual encoding of emotions in interactive bodily expressions. iScience, 27(1), 108548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2023.108548
Christensen, A., Taubert, N., Veld, E. M. J. H. I. ’., de Gelder, B., & Giese, M. A. (2024). Perceptual encoding of emotions in interactive bodily expressions. iScience, 27(1), 108548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2023.108548
 Schiller, D., Yu, A. N., Alia‐Klein, N., Becker, S., Cromwell, H. C., Dolcos, F., Eslinger, P. J., Frewen, P. A., Kemp, A. H., Pace‐Schott, E. F., Raber, J., Silton, R. L., Stefanova, E., Williams, J. H. G., Abe, N., Aghajani, M., Albrecht, F., Alexander, R., Anders, S., . . . Leonie, L. (2024). The human affectome. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 158, 105450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105450
Schiller, D., Yu, A. N., Alia‐Klein, N., Becker, S., Cromwell, H. C., Dolcos, F., Eslinger, P. J., Frewen, P. A., Kemp, A. H., Pace‐Schott, E. F., Raber, J., Silton, R. L., Stefanova, E., Williams, J. H. G., Abe, N., Aghajani, M., Albrecht, F., Alexander, R., Anders, S., . . . Leonie, L. (2024). The human affectome. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 158, 105450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105450
 Burgio, F., Menardi, A., Benavides-Varela, S., Danesin, L., Giustiniani, A., Van Den Stock, J., De Mitri, R., Biundo, R., Meneghello, F., Antonini, A., Vallesi, A., de Gelder, B., & Semenza, C. (2024). Facial emotion recognition in individuals with mild cognitive impairment: An exploratory study. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-024-01160-5
Burgio, F., Menardi, A., Benavides-Varela, S., Danesin, L., Giustiniani, A., Van Den Stock, J., De Mitri, R., Biundo, R., Meneghello, F., Antonini, A., Vallesi, A., de Gelder, B., & Semenza, C. (2024). Facial emotion recognition in individuals with mild cognitive impairment: An exploratory study. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-024-01160-5
2023
 Vandenbulcke, M., Van de Vliet, L., Sun, J., Huang, Y. A., Van Den Bossche, M. J., Sunaert, S., ... & Van den Stock, J. (2023). A paleo-neurologic investigation of the social brain hypothesis in frontotemporal dementia. Cerebral Cortex, 33(3), 622-633. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhac089
Vandenbulcke, M., Van de Vliet, L., Sun, J., Huang, Y. A., Van Den Bossche, M. J., Sunaert, S., ... & Van den Stock, J. (2023). A paleo-neurologic investigation of the social brain hypothesis in frontotemporal dementia. Cerebral Cortex, 33(3), 622-633. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhac089
 Poyo Solanas, M., Zhan, M., & de Gelder, B. (2023). Gradual relation between perceptual awareness, recognition and pupillary responses to social threat. Current Research in Behavioral Sciences, 100134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crbeha.2023.100134
Poyo Solanas, M., Zhan, M., & de Gelder, B. (2023). Gradual relation between perceptual awareness, recognition and pupillary responses to social threat. Current Research in Behavioral Sciences, 100134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crbeha.2023.100134
 David, C., Casilli, A. A., Delanoë, A., de Rosnay, M. D., de Gelder, B., Frau-Meigs, D., ... & Chavalarias, D. (2023). Toward a Research Agenda on Digital Media and Humanity Well-Being.
David, C., Casilli, A. A., Delanoë, A., de Rosnay, M. D., de Gelder, B., Frau-Meigs, D., ... & Chavalarias, D. (2023). Toward a Research Agenda on Digital Media and Humanity Well-Being.
 Lu, J., Kemmerer, S. K., Riecke, L. & de Gelder, B. (2023). Early threat perception is independent of later cognitive and behavioral control. A virtual reality-EEG-ECG study. Cerebral Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhad156
Lu, J., Kemmerer, S. K., Riecke, L. & de Gelder, B. (2023). Early threat perception is independent of later cognitive and behavioral control. A virtual reality-EEG-ECG study. Cerebral Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhad156
 Bognár, A., Raman, R., Taubert, N., Zafirova, Y., Li, B., Giese, M., de Gelder, B., Vogels, R. (2023). The contribution of dynamics to macaque body and face patch responses. NeuroImage, 119907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.119907
Bognár, A., Raman, R., Taubert, N., Zafirova, Y., Li, B., Giese, M., de Gelder, B., Vogels, R. (2023). The contribution of dynamics to macaque body and face patch responses. NeuroImage, 119907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.119907
 de Gelder, B. (2023). Social affordances, mirror neurons, and how to understand the social brain. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2022.11.011
de Gelder, B. (2023). Social affordances, mirror neurons, and how to understand the social brain. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2022.11.011
 de Gelder, B., Poyo Solanas, M., Seinfeld, S. (2023). The Aggressive Body. Understanding Aggression Combining Virtual Reality, Computational Movement Features, and Neuroimaging. In: Martin, C., Preedy, V.R., Patel, V.B. (eds) Handbook of Anger, Aggression, and Violence. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98711-4_99-1
de Gelder, B., Poyo Solanas, M., Seinfeld, S. (2023). The Aggressive Body. Understanding Aggression Combining Virtual Reality, Computational Movement Features, and Neuroimaging. In: Martin, C., Preedy, V.R., Patel, V.B. (eds) Handbook of Anger, Aggression, and Violence. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98711-4_99-1
 Marrazzo, G., De Martino, F., Lage-Castellanos, A., Vaessen, M. J., & de Gelder, B. (2023). Voxelwise encoding models of body stimuli reveal a representational gradient from low-level visual features to postural features in occipitotemporal cortex. NeuroImage, 120240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120240
Marrazzo, G., De Martino, F., Lage-Castellanos, A., Vaessen, M. J., & de Gelder, B. (2023). Voxelwise encoding models of body stimuli reveal a representational gradient from low-level visual features to postural features in occipitotemporal cortex. NeuroImage, 120240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120240
 Li, B., Poyo Solanas, M., Marrazzo, G., Raman, R., Taubert, N., Giese, M., ... & de Gelder, B. (2023). A large-scale brain network of species-specific dynamic human body perception. Progress in Neurobiology, 102398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2022.102398
Li, B., Poyo Solanas, M., Marrazzo, G., Raman, R., Taubert, N., Giese, M., ... & de Gelder, B. (2023). A large-scale brain network of species-specific dynamic human body perception. Progress in Neurobiology, 102398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2022.102398
2022
 Seinfeld, S., Hortensius, R., Arroyo-Palacios, J., Iruretagoyena, G., Zapata, L. E., de Gelder, B., ... & Sanchez-Vives, M. V. (2022). Domestic violence from a child perspective: impact of an immersive virtual reality experience on men with a history of intimate partner violent behavior. Journal of interpersonal violence, 08862605221106130. https://doi.org/10.1177/08862605221106130
Seinfeld, S., Hortensius, R., Arroyo-Palacios, J., Iruretagoyena, G., Zapata, L. E., de Gelder, B., ... & Sanchez-Vives, M. V. (2022). Domestic violence from a child perspective: impact of an immersive virtual reality experience on men with a history of intimate partner violent behavior. Journal of interpersonal violence, 08862605221106130. https://doi.org/10.1177/08862605221106130
 de Borst, A. W., & de Gelder, B. (2022). Threat Detection in Nearby Space Mobilizes Human Ventral Premotor Cortex, Intraparietal Sulcus, and Amygdala. Brain Sciences, 12(3), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12030391
de Borst, A. W., & de Gelder, B. (2022). Threat Detection in Nearby Space Mobilizes Human Ventral Premotor Cortex, Intraparietal Sulcus, and Amygdala. Brain Sciences, 12(3), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12030391
 de Gelder, B., & Poyo Solanas, M.(2022). What postures communicate. Enfance, 3(3), 353-365.https://doi.org/10.3917/enf2.223.0353
de Gelder, B., & Poyo Solanas, M.(2022). What postures communicate. Enfance, 3(3), 353-365.https://doi.org/10.3917/enf2.223.0353
 de Gelder, B., Zhan, M., & Van den Stock, J. (2022). Acquired Prosopagnosia with Structurally Intact and Functional Fusiform Face Area and with Face Identity-Specific Configuration Processing Deficits. Cerebral Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhab509
de Gelder, B., Zhan, M., & Van den Stock, J. (2022). Acquired Prosopagnosia with Structurally Intact and Functional Fusiform Face Area and with Face Identity-Specific Configuration Processing Deficits. Cerebral Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhab509
 Mello, M., Dupont, L., Engelen, T., Acciarino, A., de Borst, A. W., & de Gelder, B. (2022). The influence of body expression, group affiliation and threat proximity on interactions in virtual reality. Current Research in Behavioral Sciences, 3, 100075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crbeha.2022.100075
Mello, M., Dupont, L., Engelen, T., Acciarino, A., de Borst, A. W., & de Gelder, B. (2022). The influence of body expression, group affiliation and threat proximity on interactions in virtual reality. Current Research in Behavioral Sciences, 3, 100075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crbeha.2022.100075
 Tursic, A., Vaessen, M., Zhan, M., Vingerhoets, A. J., & de Gelder, B. (2022). The power of tears: Observers’ brain responses show that tears provide unambiguous signals independent of scene context. Neuroimage: Reports, 2(3), 100105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ynirp.2022.100105
Tursic, A., Vaessen, M., Zhan, M., Vingerhoets, A. J., & de Gelder, B. (2022). The power of tears: Observers’ brain responses show that tears provide unambiguous signals independent of scene context. Neuroimage: Reports, 2(3), 100105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ynirp.2022.100105
 Vandenbulcke, M., Van de Vliet, L., Sun, J., Huang, Y. A., Van Den Bossche, M. J., Sunaert, S., ... & Van den Stock, J. (2022). A paleo-neurologic investigation of the social brain hypothesis in frontotemporal dementia. Cerebral Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhac089
Vandenbulcke, M., Van de Vliet, L., Sun, J., Huang, Y. A., Van Den Bossche, M. J., Sunaert, S., ... & Van den Stock, J. (2022). A paleo-neurologic investigation of the social brain hypothesis in frontotemporal dementia. Cerebral Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhac089
2021
 Bobes, M. A., Van den Stock, J., Zhan, M., Valdes-Sosa, M., & de Gelder, B. (2021). Looking beyond indirect lesion network mapping of prosopagnosia: direct measures required. Brain, 144(9), e75-e75. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awab276
Bobes, M. A., Van den Stock, J., Zhan, M., Valdes-Sosa, M., & de Gelder, B. (2021). Looking beyond indirect lesion network mapping of prosopagnosia: direct measures required. Brain, 144(9), e75-e75. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awab276
 de Gelder, B., & Poyo Solanas, M.(2021). A computational neuroethology perspective on body and expression perception. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 25(9), 744-756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2021.05.010
de Gelder, B., & Poyo Solanas, M.(2021). A computational neuroethology perspective on body and expression perception. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 25(9), 744-756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2021.05.010
 Dukes, D., Abrams, K., Adolphs, R., Ahmed, M. E., Beatty, A., Berridge, K. C., ... & Sander, D. (2021). The rise of affectivism. Nature human behaviour, 5(7), 816-820. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01130-8
Dukes, D., Abrams, K., Adolphs, R., Ahmed, M. E., Beatty, A., Berridge, K. C., ... & Sander, D. (2021). The rise of affectivism. Nature human behaviour, 5(7), 816-820. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01130-8
 Marrazzo, G., Vaessen, M. J., & de Gelder, B. (2021). Decoding the difference between explicit and implicit body expression representation in high level visual, prefrontal and inferior parietal cortex. NeuroImage, 243, 118545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118545
Marrazzo, G., Vaessen, M. J., & de Gelder, B. (2021). Decoding the difference between explicit and implicit body expression representation in high level visual, prefrontal and inferior parietal cortex. NeuroImage, 243, 118545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118545
 Olugbade, T., Sagoleo, R., Ghisio, S., Gold, N., Amanda, C. D. C., De Gelder, B., ... & Bianchi-Berthouze, N. (2021, September). The AffectMove 2021 Challenge-Affect Recognition from Naturalistic Movement Data. In 2021 9th International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction Workshops and Demos (ACIIW) (pp. 01-05). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACIIW52867.2021.9666322
Olugbade, T., Sagoleo, R., Ghisio, S., Gold, N., Amanda, C. D. C., De Gelder, B., ... & Bianchi-Berthouze, N. (2021, September). The AffectMove 2021 Challenge-Affect Recognition from Naturalistic Movement Data. In 2021 9th International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction Workshops and Demos (ACIIW) (pp. 01-05). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACIIW52867.2021.9666322
 Seinfeld, S., Zhan, M., Poyo Solanas, M., Barsuola, G., Vaessen, M., Slater, M., ... & de Gelder, B. (2021). Being the victim of virtual abuse changes default mode network responses to emotional expressions. cortex, 135, 268-284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2020.11.018
Seinfeld, S., Zhan, M., Poyo Solanas, M., Barsuola, G., Vaessen, M., Slater, M., ... & de Gelder, B. (2021). Being the victim of virtual abuse changes default mode network responses to emotional expressions. cortex, 135, 268-284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2020.11.018
2020
 Poyo Solanas, M., Vaessen, M., & de Gelder, B. (2020). Computation-Based Feature Representation of Body Expressions in the Human Brain. Cerebral Cortex, 30(12), 6376-6390. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhaa196
Poyo Solanas, M., Vaessen, M., & de Gelder, B. (2020). Computation-Based Feature Representation of Body Expressions in the Human Brain. Cerebral Cortex, 30(12), 6376-6390. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhaa196
 Poyo Solanas, M., Vaessen, M. J., & de Gelder, B. (2020). The role of computational and subjective features in emotional body expressions. Scientific reports, 10(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63125-1
Poyo Solanas, M., Vaessen, M. J., & de Gelder, B. (2020). The role of computational and subjective features in emotional body expressions. Scientific reports, 10(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63125-1
 Lenzoni, S., Bozzoni, V., Burgio, F., de Gelder, B., Wennberg, A., Botta, A., ... & Semenza, C. (2020). Recognition of emotions conveyed by facial expression and body postures in myotonic dystrophy (DM). Cortex, 127, 58-66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2020.02.005
Lenzoni, S., Bozzoni, V., Burgio, F., de Gelder, B., Wennberg, A., Botta, A., ... & Semenza, C. (2020). Recognition of emotions conveyed by facial expression and body postures in myotonic dystrophy (DM). Cortex, 127, 58-66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2020.02.005
 de Borst, A. W., Sanchez-Vives, M. V., Slater, M., & de Gelder, B. (2020). First-Person Virtual Embodiment Modulates the Cortical Network that Encodes the Bodily Self and Its Surrounding Space during the Experience of Domestic Violence. Eneuro, 7(3). https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0263-19.2019
de Borst, A. W., Sanchez-Vives, M. V., Slater, M., & de Gelder, B. (2020). First-Person Virtual Embodiment Modulates the Cortical Network that Encodes the Bodily Self and Its Surrounding Space during the Experience of Domestic Violence. Eneuro, 7(3). https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0263-19.2019
 Ross, P., de Gelder, B., Crabbe, F., & Grosbras, M. H. (2020). A Dynamic Body-Selective Area Localizer for use in fMRI. MethodsX, 100801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2020.100801
Ross, P., de Gelder, B., Crabbe, F., & Grosbras, M. H. (2020). A Dynamic Body-Selective Area Localizer for use in fMRI. MethodsX, 100801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2020.100801
 Dolcos, F., Katsumi, Y., Moore, M., Berggren, N., de Gelder, B., Derakshan, N., ... & Pegna, A. J. (2020). Neural Correlates of Emotion-Attention Interactions: From Perception, Learning and Memory to Individual Differences and Training Interventions. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 108: 559-601, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.08.017
Dolcos, F., Katsumi, Y., Moore, M., Berggren, N., de Gelder, B., Derakshan, N., ... & Pegna, A. J. (2020). Neural Correlates of Emotion-Attention Interactions: From Perception, Learning and Memory to Individual Differences and Training Interventions. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 108: 559-601, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.08.017
 Van Der Heijden, K., Formisano, E., Valente, G., Zhan, M., Kupers, R., & De Gelder, B. (2020). Reorganization of sound location processing in the auditory cortex of blind humans. Cerebral Cortex, 30(3), 1103-1116. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhz151
Van Der Heijden, K., Formisano, E., Valente, G., Zhan, M., Kupers, R., & De Gelder, B. (2020). Reorganization of sound location processing in the auditory cortex of blind humans. Cerebral Cortex, 30(3), 1103-1116. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhz151
 Kätsyri, J., de Gelder, B., & de Borst, A. W. (2020). Amygdala responds to direct gaze in real but not in computer-generated faces. NeuroImage, 204, 116216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116216
Kätsyri, J., de Gelder, B., & de Borst, A. W. (2020). Amygdala responds to direct gaze in real but not in computer-generated faces. NeuroImage, 204, 116216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116216
 Watson, R. & de Gelder, B. (2019). The representation and plasticity of body emotion expression. Psychological Research,1-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-018-1133-1
Watson, R. & de Gelder, B. (2019). The representation and plasticity of body emotion expression. Psychological Research,1-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-018-1133-1
2019
 Koizumi, A., Zhan, M., Ban, H., Kida, I., De Martino, F., Vaessen, M. J., de Gelder, B., Amano, K. (2019). Threat anticipation in pulvinar and in superficial layers of primary visual cortex (V1). Evidence from layer-specific ultra-high field 7T fMRI. eNeuro, 6(6). https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0429-19.2019
Koizumi, A., Zhan, M., Ban, H., Kida, I., De Martino, F., Vaessen, M. J., de Gelder, B., Amano, K. (2019). Threat anticipation in pulvinar and in superficial layers of primary visual cortex (V1). Evidence from layer-specific ultra-high field 7T fMRI. eNeuro, 6(6). https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0429-19.2019
 Zhan, M., Engelen, T., & de Gelder, B. (2019). Influence of continuous flash suppression mask frequency on stimulus visibility. Neuropsychologia, 128, 65-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.05.012
Zhan, M., Engelen, T., & de Gelder, B. (2019). Influence of continuous flash suppression mask frequency on stimulus visibility. Neuropsychologia, 128, 65-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.05.012
 Ross, P., de Gelder, B., Crabbe, F., & Grosbras, M. H. (2019). Emotion modulation of the body-selective areas in the developing brain. Developmental cognitive neuroscience, 38, 100660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2019.100660
Ross, P., de Gelder, B., Crabbe, F., & Grosbras, M. H. (2019). Emotion modulation of the body-selective areas in the developing brain. Developmental cognitive neuroscience, 38, 100660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2019.100660
 Kätsyri, J., de Gelder, B., & Takala, T. (2019). Virtual faces evoke only a weak uncanny valley effect: An empirical investigation with controlled virtual face images. Perception, 48(10), 968-991. https://doi.org/10.1177/0301006619869134
Kätsyri, J., de Gelder, B., & Takala, T. (2019). Virtual faces evoke only a weak uncanny valley effect: An empirical investigation with controlled virtual face images. Perception, 48(10), 968-991. https://doi.org/10.1177/0301006619869134
 Van der Heijden, K., Rauschecker, J.P., de Gelder, B., Formisano, E. (2019) Cortical mechanisms of spatial hearing. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 20:609–623. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0206-5
Van der Heijden, K., Rauschecker, J.P., de Gelder, B., Formisano, E. (2019) Cortical mechanisms of spatial hearing. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 20:609–623. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0206-5
 Zhan, M., & de Gelder, B. (2019). Unconscious fearful body expression perception enhances discrimination of conscious anger expressions under continuous flash suppression. Neuropsychologia, 128:325-331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.04.019
Zhan, M., & de Gelder, B. (2019). Unconscious fearful body expression perception enhances discrimination of conscious anger expressions under continuous flash suppression. Neuropsychologia, 128:325-331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.04.019
 Burra, N., Hervais-Adelman, A., Celeghin, A., de Gelder, B. (2019). Affective Blindsight relies on Low Spatial Frequencies. Neuropsychologia, 128:44-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.10.009
Burra, N., Hervais-Adelman, A., Celeghin, A., de Gelder, B. (2019). Affective Blindsight relies on Low Spatial Frequencies. Neuropsychologia, 128:44-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.10.009
2018
 Dayan, E., Barliya, A., de Gelder, B., Hendler, T., Malach, R., & Flash, T. (2018). Motion cues modulate responses to emotion in movies. Scientific reports, 8(1), 10881. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29111-4
Dayan, E., Barliya, A., de Gelder, B., Hendler, T., Malach, R., & Flash, T. (2018). Motion cues modulate responses to emotion in movies. Scientific reports, 8(1), 10881. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29111-4
 Hortensius, R., & Gelder, B. de. (2018). From Empathy to Apathy: The Bystander Effect Revisited. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 27(4), 249–256. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721417749653
Hortensius, R., & Gelder, B. de. (2018). From Empathy to Apathy: The Bystander Effect Revisited. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 27(4), 249–256. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721417749653
 Engelen, T., Zhan, M., Sack, A.T., & de Gelder, B. (2018).The Influence of Conscious and Unconscious Body Threat Expressions on Motor Evoked Potentials Studied With Continuous Flash Suppression. Front. Neurosci. 12:480. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00480
Engelen, T., Zhan, M., Sack, A.T., & de Gelder, B. (2018).The Influence of Conscious and Unconscious Body Threat Expressions on Motor Evoked Potentials Studied With Continuous Flash Suppression. Front. Neurosci. 12:480. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00480
 Van der Heijden, K., Rauschecker, J. P., Formisano, E., Valente, G., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Active sound localization sharpens spatial tuning in human primary auditory cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 38(40), 8574-8587. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0587-18.2018
Van der Heijden, K., Rauschecker, J. P., Formisano, E., Valente, G., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Active sound localization sharpens spatial tuning in human primary auditory cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 38(40), 8574-8587. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0587-18.2018
 de Gelder, B., Watson, R., Zhan, M., Diano, M., Tamietto, M., & Vaessen, M. J. (2018). Classical paintings may trigger pain and pleasure in the gendered brain. Cortex, 109, 171-180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2018.09.011
de Gelder, B., Watson, R., Zhan, M., Diano, M., Tamietto, M., & Vaessen, M. J. (2018). Classical paintings may trigger pain and pleasure in the gendered brain. Cortex, 109, 171-180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2018.09.011
 Terburg,D., Scheggia, D., Triana del Rio,R., Klumpers, F., Cristian Ciobanu, A., Morgan, B., Montoya, E.R., Bos, P.A., Giobellina, G, van den Burg, E., de Gelder, B., Stein, D.J., Stoop, R. & van Honk, J.(2018). The basolateral amygdala is essential for rapid escape behavior: a human-rodent study. Cell, 175(3): 723-735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.028
Terburg,D., Scheggia, D., Triana del Rio,R., Klumpers, F., Cristian Ciobanu, A., Morgan, B., Montoya, E.R., Bos, P.A., Giobellina, G, van den Burg, E., de Gelder, B., Stein, D.J., Stoop, R. & van Honk, J.(2018). The basolateral amygdala is essential for rapid escape behavior: a human-rodent study. Cell, 175(3): 723-735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.028
 Vaessen, M.J., Abassi, E., Mancini, M., Camurri, A., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Computational feature analysis of body movements reveals hierarchical brain organization. Cerebral Cortex, bhy228, https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhy228
Vaessen, M.J., Abassi, E., Mancini, M., Camurri, A., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Computational feature analysis of body movements reveals hierarchical brain organization. Cerebral Cortex, bhy228, https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhy228
 de Borst, A.W., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Mental imagery follows similar cortical reorganization as perception: intra-modal and cross-modal plasticity in congenitally blind. Cerebral Cortex, bhy151. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhy151
de Borst, A.W., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Mental imagery follows similar cortical reorganization as perception: intra-modal and cross-modal plasticity in congenitally blind. Cerebral Cortex, bhy151. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhy151
 Engelen, T., Zhan, M., Sack, A.T., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Dynamic Interactions between Emotion Perception and Action Preparation for Reacting to Social Threat: A Combined cTBS-fMRI Study. eNeuro, ENEURO-0408. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0408-17.2018
Engelen, T., Zhan, M., Sack, A.T., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Dynamic Interactions between Emotion Perception and Action Preparation for Reacting to Social Threat: A Combined cTBS-fMRI Study. eNeuro, ENEURO-0408. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0408-17.2018
 de Gelder, B. & Van den Stock, J. (2018) Face specificity of developmental prosopagnosia, moving beyond the debate on face specificity, Cognitive Neuropsychology, 35:1-2, 87-89. https://doi.org/10.1080/02643294.2018.1441818
de Gelder, B. & Van den Stock, J. (2018) Face specificity of developmental prosopagnosia, moving beyond the debate on face specificity, Cognitive Neuropsychology, 35:1-2, 87-89. https://doi.org/10.1080/02643294.2018.1441818
 de Gelder, B., Kätsyri, J., & de Borst, A. W. (2018) Virtual reality and the new psychophysics. British Journal of Psychology, 109, 421-426. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/bjop.12308; For open access (PsyArXiv Preprint) click here: doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/tdmyu.
de Gelder, B., Kätsyri, J., & de Borst, A. W. (2018) Virtual reality and the new psychophysics. British Journal of Psychology, 109, 421-426. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/bjop.12308; For open access (PsyArXiv Preprint) click here: doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/tdmyu.
 Schilberg, L., Engelen, T., ten Oever, S., Schuhmann, T., de Gelder, B.,de Graaf, T.A. & Sack, A.T. (2018). Phase of beta-frequency tACS over primary motor cortex modulates corticospinal excitability. Cortex, 103, 142-152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2018.03.001
Schilberg, L., Engelen, T., ten Oever, S., Schuhmann, T., de Gelder, B.,de Graaf, T.A. & Sack, A.T. (2018). Phase of beta-frequency tACS over primary motor cortex modulates corticospinal excitability. Cortex, 103, 142-152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2018.03.001
 Hortensius R., Neyret S., Slater M., & de Gelder, B. (in press). The relation between bystanders' behavioral reactivity to distress and later helping behavior during a violent conflict in virtual reality. PLoS ONE, 13(4): e0196074. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196074
Hortensius R., Neyret S., Slater M., & de Gelder, B. (in press). The relation between bystanders' behavioral reactivity to distress and later helping behavior during a violent conflict in virtual reality. PLoS ONE, 13(4): e0196074. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196074
 Zhan, M., Goebel, R., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Ventral and Dorsal Pathways Relate Differently to Visual Awareness of Body Postures under Continuous Flash Suppression. eNeuro, 5(1), ENEURO-0285. http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0285-17.2017
Zhan, M., Goebel, R., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Ventral and Dorsal Pathways Relate Differently to Visual Awareness of Body Postures under Continuous Flash Suppression. eNeuro, 5(1), ENEURO-0285. http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0285-17.2017
 Seinfeld,S., Arroyo-Palacios,J., Iruretagoyena, G., Hortenisus,R., Zapata, L.E., Borland, D., de Gelder,B., Slater, M., & Sanchez-Vives, M.V. (2018). Offenders become the victim in virtual reality: impact of changing perspective in domestic violence. Scientific reports, 8, 2692. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19987-7
Seinfeld,S., Arroyo-Palacios,J., Iruretagoyena, G., Hortenisus,R., Zapata, L.E., Borland, D., de Gelder,B., Slater, M., & Sanchez-Vives, M.V. (2018). Offenders become the victim in virtual reality: impact of changing perspective in domestic violence. Scientific reports, 8, 2692. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19987-7
 Sellaro, R., de Gelder, B, Finisguerra, A., Colzato, L.S. (2018). Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) enhances recognition of emotions in faces but not bodies. Cortex, 99, 213-223 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2017.11.007
Sellaro, R., de Gelder, B, Finisguerra, A., Colzato, L.S. (2018). Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) enhances recognition of emotions in faces but not bodies. Cortex, 99, 213-223 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2017.11.007
 Poyo Solanas, M., Zhan, M., Vaessen, M., Hortensius, R., Engelen, T., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Looking at the face and seeing the whole body. Neural basis of combined face and body expressions, Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 13(1), 135-144. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsx130
Poyo Solanas, M., Zhan, M., Vaessen, M., Hortensius, R., Engelen, T., & de Gelder, B. (2018). Looking at the face and seeing the whole body. Neural basis of combined face and body expressions, Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 13(1), 135-144. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsx130
Chapter
 de Gelder B. & Tamietto, M. (2018). What is the role of conscious awareness in emotion? In: The nature of emotion. Oxford University Press
de Gelder B. & Tamietto, M. (2018). What is the role of conscious awareness in emotion? In: The nature of emotion. Oxford University Press
2017
 Celeghin, A., Diano, M., de Gelder, B., Weiskrantz, L., Marzi, C.A. & Tamietto, M. (2017). Intact hemisphere and corpus callosum compensate for visuo-motor functions after visual cortex damage. PNAS,114(48), E10475–E10483. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1714801114
Celeghin, A., Diano, M., de Gelder, B., Weiskrantz, L., Marzi, C.A. & Tamietto, M. (2017). Intact hemisphere and corpus callosum compensate for visuo-motor functions after visual cortex damage. PNAS,114(48), E10475–E10483. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1714801114
 Engelen,T., Watson, R., Pavani, F., de Gelder, B. (2017). Affective vocalizations influence body ownership as measured in the rubber hand illusion. PloS ONE, 12(10), e0186009. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186009
Engelen,T., Watson, R., Pavani, F., de Gelder, B. (2017). Affective vocalizations influence body ownership as measured in the rubber hand illusion. PloS ONE, 12(10), e0186009. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186009
 Derey, K., Rauschecker, J. P., Formisano, E., Valente, G., de Gelder, B. (2017). Localization of complex sounds is modulated by behavioral relevance and sound category. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 142(4), 1757–1773. http://dx.doi.org/10.1121/1.5003779
Derey, K., Rauschecker, J. P., Formisano, E., Valente, G., de Gelder, B. (2017). Localization of complex sounds is modulated by behavioral relevance and sound category. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 142(4), 1757–1773. http://dx.doi.org/10.1121/1.5003779
 de Gelder, B. (2017). Going Native. Emotion Science in the Twenty-First Century. Frontiers in Psychology, 8,1212. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01212
de Gelder, B. (2017). Going Native. Emotion Science in the Twenty-First Century. Frontiers in Psychology, 8,1212. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01212
 Trinkler, I., Devignevielle, S., Achaibou, A., Ligneul, R. V., Brugières, P., de Langavant, L. C., de Gelder, B... & Bachoud-Lévi, A. C. (2017). Embodied emotion impairment in Huntington's Disease. Cortex, 92, 44-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2017.02.019
Trinkler, I., Devignevielle, S., Achaibou, A., Ligneul, R. V., Brugières, P., de Langavant, L. C., de Gelder, B... & Bachoud-Lévi, A. C. (2017). Embodied emotion impairment in Huntington's Disease. Cortex, 92, 44-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2017.02.019
 Tipura, E., Pegna, A. J., de Gelder, B., & Renaud, O. (2017). Visual stimuli modulate frontal oscillatory rhythms in a cortically blind patient: Evidence for top-down visual processing. Clinical Neurophysiology, 128(5), 770-779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.02.009
Tipura, E., Pegna, A. J., de Gelder, B., & Renaud, O. (2017). Visual stimuli modulate frontal oscillatory rhythms in a cortically blind patient: Evidence for top-down visual processing. Clinical Neurophysiology, 128(5), 770-779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.02.009
 Hortensius, R., Terburg, D., Morgan, B., Stein, D. J., van Honk, J., & de Gelder, B. (2017). The basolateral amygdalae and frontotemporal network functions for threat perception. eNeuro,4(1), ENEURO-0314-16. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0314-16.2016
Hortensius, R., Terburg, D., Morgan, B., Stein, D. J., van Honk, J., & de Gelder, B. (2017). The basolateral amygdalae and frontotemporal network functions for threat perception. eNeuro,4(1), ENEURO-0314-16. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0314-16.2016
 Watson, R. & de Gelder, B. (2017). How white and black bodies are perceived depends on what emotion is expressed. Scientific Reports,7,41349. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41349
Watson, R. & de Gelder, B. (2017). How white and black bodies are perceived depends on what emotion is expressed. Scientific Reports,7,41349. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41349
 Hortensius, R., Terburg, D., Morgan, B., Stein, D. J., van Honk, J., & de Gelder, B. (2017). The dynamic consequences of amygdala damage on threat processing in Urbach–Wiethe Disease. A commentary on Pishnamazi et al.(2016). Cortex,88,192-197 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2016.07.013
Hortensius, R., Terburg, D., Morgan, B., Stein, D. J., van Honk, J., & de Gelder, B. (2017). The dynamic consequences of amygdala damage on threat processing in Urbach–Wiethe Disease. A commentary on Pishnamazi et al.(2016). Cortex,88,192-197 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2016.07.013
 de Borst, A. W., & de Gelder, B. (2017). fMRI-based multivariate pattern analyses reveal imagery modality and imagery content specific representations in primary somatosensory, motor and auditory cortices. Cerebral Cortex, 27(8), 3994-4009. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw211
de Borst, A. W., & de Gelder, B. (2017). fMRI-based multivariate pattern analyses reveal imagery modality and imagery content specific representations in primary somatosensory, motor and auditory cortices. Cerebral Cortex, 27(8), 3994-4009. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw211
2016
 De Winter, F. L., Van den Stock, J., de Gelder, B., Peeters, R., Jastorff, J., Sunaert, S., Vanduffel, W., Vandenberghe, R., Vandenbulcke, M. (2016). Amygdala atrophy affects emotion-related activity in face-responsive regions in frontotemporal degeneration. Cortex, 82, 179-191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2016.06.001
De Winter, F. L., Van den Stock, J., de Gelder, B., Peeters, R., Jastorff, J., Sunaert, S., Vanduffel, W., Vandenberghe, R., Vandenbulcke, M. (2016). Amygdala atrophy affects emotion-related activity in face-responsive regions in frontotemporal degeneration. Cortex, 82, 179-191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2016.06.001
 Hortensius R., de Gelder B & Schutter D.J.L.G. (2016). When anger dominates the mind – increased motor corticospinal excitability in the face of threat. Psychophysiology, 53, 1307-1316. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.12685
Hortensius R., de Gelder B & Schutter D.J.L.G. (2016). When anger dominates the mind – increased motor corticospinal excitability in the face of threat. Psychophysiology, 53, 1307-1316. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.12685
 Hortensius, R., Schutter, D. J., & de Gelder, B. (2016). Personal distress and the influence of bystanders on responding to an emergency. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 16(4), 672-688. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-016-0423-6
Hortensius, R., Schutter, D. J., & de Gelder, B. (2016). Personal distress and the influence of bystanders on responding to an emergency. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 16(4), 672-688. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-016-0423-6
 Hortensius R, Terburg D, Morgan B, Stein DJ, van Honk J, de Gelder B. (2016). The role of the basolateral amygdala in the perception of faces in natural contexts. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B, 371(1693), 20150376. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0376
Hortensius R, Terburg D, Morgan B, Stein DJ, van Honk J, de Gelder B. (2016). The role of the basolateral amygdala in the perception of faces in natural contexts. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B, 371(1693), 20150376. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0376
 Meeren, H. K. M, Hadjikhani, N., Ahlfors, S.P., Hämäläinen, M.S., de Gelder B. (2016). Early preferential responses to fear stimuli in human right dorsal visual stream measured with MEG. Scientific Reports, 6, 24831. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24831
Meeren, H. K. M, Hadjikhani, N., Ahlfors, S.P., Hämäläinen, M.S., de Gelder B. (2016). Early preferential responses to fear stimuli in human right dorsal visual stream measured with MEG. Scientific Reports, 6, 24831. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24831
 De Winter, F. L., Timmers, D., de Gelder, B., Van Orshoven, M., Vieren, M., Bouckaert, M., ... & Van Laere, K. (2016). Face shape and face identity processing in behavioral variant fronto-temporal dementia: A specific deficit for familiarity and name recognition of famous faces. NeuroImage: Clinical, 11, 368-377. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2016.03.001
De Winter, F. L., Timmers, D., de Gelder, B., Van Orshoven, M., Vieren, M., Bouckaert, M., ... & Van Laere, K. (2016). Face shape and face identity processing in behavioral variant fronto-temporal dementia: A specific deficit for familiarity and name recognition of famous faces. NeuroImage: Clinical, 11, 368-377. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2016.03.001
 Watson, R., Huis in 't Veld, E.M.J., & de Gelder, B. (2016). The Neural Basis of Individual Face and Object Perception. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 10, 66. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00066
Watson, R., Huis in 't Veld, E.M.J., & de Gelder, B. (2016). The Neural Basis of Individual Face and Object Perception. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 10, 66. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00066
 de Borst, A.W., de Gelder, B. (2016). Clear signals or mixed messages: Inter-individual emotion congruency modulates brain activity underlying affective body perception. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 11(8), 1299-309. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsw039
de Borst, A.W., de Gelder, B. (2016). Clear signals or mixed messages: Inter-individual emotion congruency modulates brain activity underlying affective body perception. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 11(8), 1299-309. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsw039
Book
 de Gelder, B. (2016). Emotions and the Body. Oxford University Press.
de Gelder, B. (2016). Emotions and the Body. Oxford University Press.
Chapter
 de Gelder, B. & Huis in 't Veld, E.M.J. (2016). Cultural differences in emotional expressions and body language. In Chiao, J.Y. (Eds.), Handbook of Cultural Neuroscience. Oxford University Press, pp.223-234
de Gelder, B. & Huis in 't Veld, E.M.J. (2016). Cultural differences in emotional expressions and body language. In Chiao, J.Y. (Eds.), Handbook of Cultural Neuroscience. Oxford University Press, pp.223-234
 de Gelder, B. (2016) Emotional body perception in the wild. In Barrett, L. F. (Eds.). Handbook of emotions. Guilford Publications, pp. 483-494
de Gelder, B. (2016) Emotional body perception in the wild. In Barrett, L. F. (Eds.). Handbook of emotions. Guilford Publications, pp. 483-494
2015
 Seirafi, M., De Weerd, P., Pegna, A. J., de Gelder, B. (2015). Audiovisual Blindsight: Audiovisual learning in the absence of primary visual cortex. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 686. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00686
Seirafi, M., De Weerd, P., Pegna, A. J., de Gelder, B. (2015). Audiovisual Blindsight: Audiovisual learning in the absence of primary visual cortex. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 686. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00686
 Kret, M. E., Stekelenburg, J. J., de Gelder, B., & Roelofs, K. (2015). From face to hand: Attentional bias towards expressive hands in social anxiety. Biological psychology, 122, 42-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2015.11.016
Kret, M. E., Stekelenburg, J. J., de Gelder, B., & Roelofs, K. (2015). From face to hand: Attentional bias towards expressive hands in social anxiety. Biological psychology, 122, 42-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2015.11.016
 de Gelder, B, Huis In 'T Veld, E.M., van den Stock, J. (2015).The Facial Expressive Action Stimulus Test. A test battery for the assessment of face memory, face and object perception, configuration processing and facial expression recognition. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1609. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01609
de Gelder, B, Huis In 'T Veld, E.M., van den Stock, J. (2015).The Facial Expressive Action Stimulus Test. A test battery for the assessment of face memory, face and object perception, configuration processing and facial expression recognition. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1609. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01609
 Hervais-Adelman, A., Legrand, LB., Zhan, M., Tamietto, M., de Gelder, B., Pegna, A. (2015). Looming sensitive cortical regions without V1 input: evidence from a patient with bilateral cortical blindness. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 9, 51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2015.00051
Hervais-Adelman, A., Legrand, LB., Zhan, M., Tamietto, M., de Gelder, B., Pegna, A. (2015). Looming sensitive cortical regions without V1 input: evidence from a patient with bilateral cortical blindness. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 9, 51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2015.00051
 Derey, K., Valente, G., de Gelder, B., Formisano, E. (2015). Opponent coding of sound location (azimuth) in planum temporale is robust to sound level variations. Cerebral Cortex, 26(1), 450-464. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhv269
Derey, K., Valente, G., de Gelder, B., Formisano, E. (2015). Opponent coding of sound location (azimuth) in planum temporale is robust to sound level variations. Cerebral Cortex, 26(1), 450-464. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhv269
 Zhan, M., Hortensius, R., de Gelder, B. (2015). The Body as a Tool for Anger Awareness—Differential Effects of Angry Facial and Bodily Expressions on Suppression from Awareness. PLoS ONE 10(10), e0139768. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139768
Zhan, M., Hortensius, R., de Gelder, B. (2015). The Body as a Tool for Anger Awareness—Differential Effects of Angry Facial and Bodily Expressions on Suppression from Awareness. PLoS ONE 10(10), e0139768. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139768
 Engelen, T., de Graaf, T. A., Sack, A. T., & de Gelder, B. (2015). A causal role for inferior parietal lobule in emotion body perception. Cortex, 73, 195-202. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2015.08.013
Engelen, T., de Graaf, T. A., Sack, A. T., & de Gelder, B. (2015). A causal role for inferior parietal lobule in emotion body perception. Cortex, 73, 195-202. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2015.08.013
 Van den Stock, J., Hortensius, R., Sinke, C., Goebel, R., & de Gelder, B. (2015). Personality traits predict brain activation and connectivity when witnessing a violent conflict. Scientific reports, 5, 13779. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13779
Van den Stock, J., Hortensius, R., Sinke, C., Goebel, R., & de Gelder, B. (2015). Personality traits predict brain activation and connectivity when witnessing a violent conflict. Scientific reports, 5, 13779. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13779
 Van den Stock, J., De Winter, F. L., de Gelder, B., Rangarajan J.R., Cypers, G., Maes, F., Sunaert, S., Goffin, K.,Vandenberghe, R., Vandenbulcke, M. (2015). Impaired recognition of body expressions in the behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia. Neuropsychologia, 75, 496-504. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.06.035
Van den Stock, J., De Winter, F. L., de Gelder, B., Rangarajan J.R., Cypers, G., Maes, F., Sunaert, S., Goffin, K.,Vandenberghe, R., Vandenbulcke, M. (2015). Impaired recognition of body expressions in the behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia. Neuropsychologia, 75, 496-504. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.06.035
 Negro E, D’Agata F, Caroppo P, Coriasco M, Ferrio F, Celeghin A, et al. (2015) Neurofunctional Signature of Hyperfamiliarity for Unknown Faces. PLoS ONE 10(7), e0129970. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129970
Negro E, D’Agata F, Caroppo P, Coriasco M, Ferrio F, Celeghin A, et al. (2015) Neurofunctional Signature of Hyperfamiliarity for Unknown Faces. PLoS ONE 10(7), e0129970. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129970
 Celeghin, A., de Gelder, B., Tamietto, M. (2015). From affective blindsight to emotional consciousness. Consciousness and Cognition, 36, 414-425. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2015.05.007
Celeghin, A., de Gelder, B., Tamietto, M. (2015). From affective blindsight to emotional consciousness. Consciousness and Cognition, 36, 414-425. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2015.05.007
 de Borst, A.W., de Gelder, B. (2015). Is it the real deal? Perception of virtual characters versus humans: an affective cognitive neuroscience perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, article 576, https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00576
de Borst, A.W., de Gelder, B. (2015). Is it the real deal? Perception of virtual characters versus humans: an affective cognitive neuroscience perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, article 576, https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00576
 Candidi M., Stienen B.M.C., Aglioti S.M., de Gelder, B. (2015). Virtual lesion of right posterior Superior Temporal Sulcus modulates conscious visual perception of fearful expressions in faces and bodies. Cortex, 65, 184-194. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2015.01.012
Candidi M., Stienen B.M.C., Aglioti S.M., de Gelder, B. (2015). Virtual lesion of right posterior Superior Temporal Sulcus modulates conscious visual perception of fearful expressions in faces and bodies. Cortex, 65, 184-194. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2015.01.012
 Huis in ‘t Veld, E. M. J. and de Gelder, B. (2015), From personal fear to mass panic: The neurological basis of crowd perception. Human Brain Mapping, 36(6), 2338-2351. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22774
Huis in ‘t Veld, E. M. J. and de Gelder, B. (2015), From personal fear to mass panic: The neurological basis of crowd perception. Human Brain Mapping, 36(6), 2338-2351. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22774
 Tamietto, M., Cauda, F., Celeghin, A., Diano, M., Costa, T., Cossa, M., Geminiani, G., Duca, S., & de Gelder, B. (2015). Once you feel it, you see it: insula and sensory-motor contribution to visual awareness for fearful bodies in parietal extinction. Cortex, 62, 56-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2014.10.009
Tamietto, M., Cauda, F., Celeghin, A., Diano, M., Costa, T., Cossa, M., Geminiani, G., Duca, S., & de Gelder, B. (2015). Once you feel it, you see it: insula and sensory-motor contribution to visual awareness for fearful bodies in parietal extinction. Cortex, 62, 56-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2014.10.009
 de Gelder, B., Tamietto, M., Pegna, A. J., & Van den Stock, J. (2015). Visual imagery influences brain responses to visual stimulation in bilateral cortical blindness. Cortex, 72, 15-26. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2014.11.009
de Gelder, B., Tamietto, M., Pegna, A. J., & Van den Stock, J. (2015). Visual imagery influences brain responses to visual stimulation in bilateral cortical blindness. Cortex, 72, 15-26. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2014.11.009
 Kristo, G., Raemaekers, M., Rutten, G. J., de Gelder, B., & Ramsey, N. F. (2015). Inter-hemispheric language functional reorganization in low-grade glioma patients after tumour surgery. Cortex, 64, 235-248. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2014.11.002
Kristo, G., Raemaekers, M., Rutten, G. J., de Gelder, B., & Ramsey, N. F. (2015). Inter-hemispheric language functional reorganization in low-grade glioma patients after tumour surgery. Cortex, 64, 235-248. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2014.11.002
 de Gelder, B., de Borst, A. W., & Watson, R. (2015). The perception of emotion in body expressions. WIREs Cogn Sci 2015, 6, 149–158. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcs.1335
de Gelder, B., de Borst, A. W., & Watson, R. (2015). The perception of emotion in body expressions. WIREs Cogn Sci 2015, 6, 149–158. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcs.1335
 Van den Stock, J., Tamietto, M., Hervais-Adelman, A., Pegna, A., & de Gelder, B. (2015). Body recognition in a patient with bilateral primary visual cortex lesions. Biological psychiatry, 77(7), e31–e33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.06.023
Van den Stock, J., Tamietto, M., Hervais-Adelman, A., Pegna, A., & de Gelder, B. (2015). Body recognition in a patient with bilateral primary visual cortex lesions. Biological psychiatry, 77(7), e31–e33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.06.023
 De Winter, F. L., Zhu, Q., Van den Stock, J., Nelissen, K., Peeters, R., de Gelder, B., Vanduffel, W., Vandenbulcke, M. (2015). Lateralization for dynamic facial expressions in human superior temporal sulcus. NeuroImage, 106, 340-352. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.11.020
De Winter, F. L., Zhu, Q., Van den Stock, J., Nelissen, K., Peeters, R., de Gelder, B., Vanduffel, W., Vandenbulcke, M. (2015). Lateralization for dynamic facial expressions in human superior temporal sulcus. NeuroImage, 106, 340-352. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.11.020
Chapter
 De Gelder, B., De Borst, A., & Watson, R. (2015). Perception des expressions émotionelles corporelles: bases neurales. In Corps en scènes (pp. 95–103). CNRS Editions.
De Gelder, B., De Borst, A., & Watson, R. (2015). Perception des expressions émotionelles corporelles: bases neurales. In Corps en scènes (pp. 95–103). CNRS Editions.
 de Gelder B., and de Borst A.W. Body Perception. In: Arthur W. Toga, editor. Brain Mapping: An Encyclopedic Reference. Academic Press: Elsevier; 2015. pp. 107-114. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-397025-1.00162-7
de Gelder B., and de Borst A.W. Body Perception. In: Arthur W. Toga, editor. Brain Mapping: An Encyclopedic Reference. Academic Press: Elsevier; 2015. pp. 107-114. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-397025-1.00162-7
 de Gelder, B., Van den Stock, J., 2015. Prosopagnosia. In: James D. Wright (editor-in-chief), International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 2nd edition, Vol 19. Oxford: Elsevier. pp. 250–255. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.56015-2
de Gelder, B., Van den Stock, J., 2015. Prosopagnosia. In: James D. Wright (editor-in-chief), International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 2nd edition, Vol 19. Oxford: Elsevier. pp. 250–255. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.56015-2
2014
 Wijnen, V.J.M., Eilander, H.J., de Gelder, B., & van Boxtel, G.J.M. (2014). Visual processing during recovery from vegetative state to consciousness: Comparing behavioral indices to brain responses. Clinical Neurophysiology, 44(5), 457-469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2014.08.008
Wijnen, V.J.M., Eilander, H.J., de Gelder, B., & van Boxtel, G.J.M. (2014). Visual processing during recovery from vegetative state to consciousness: Comparing behavioral indices to brain responses. Clinical Neurophysiology, 44(5), 457-469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2014.08.008
 Burra, N., Kerzel, D., de Gelder, B., & Pegna, A. J. (2014). Lack of automatic attentional orienting by gaze cues following a bilateral loss of visual cortex. Neuropsychologia, 58, 75-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.04.003
Burra, N., Kerzel, D., de Gelder, B., & Pegna, A. J. (2014). Lack of automatic attentional orienting by gaze cues following a bilateral loss of visual cortex. Neuropsychologia, 58, 75-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.04.003
 Wijnen, V. J., Eilander, H. J., de Gelder, B., & van Boxtel, G. J. (2014). Repeated Measurements of the Auditory Oddball Paradigm Is Related to Recovery From the Vegetative State. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology, 31(1), 65-80. doi: 10.1097/01.wnp.0000436894
Wijnen, V. J., Eilander, H. J., de Gelder, B., & van Boxtel, G. J. (2014). Repeated Measurements of the Auditory Oddball Paradigm Is Related to Recovery From the Vegetative State. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology, 31(1), 65-80. doi: 10.1097/01.wnp.0000436894
 Kristo, G., Rutten, G. J., Raemaekers, M., Gelder, B., Rombouts, S. A., & Ramsey, N. F. (2014). Task and task‐free FMRI reproducibility comparison for motor network identification. Human brain mapping, 35(1), 340-352. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22180
Kristo, G., Rutten, G. J., Raemaekers, M., Gelder, B., Rombouts, S. A., & Ramsey, N. F. (2014). Task and task‐free FMRI reproducibility comparison for motor network identification. Human brain mapping, 35(1), 340-352. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22180
 Hortensius, R., van Honk, J., de Gelder, B., & Terburg, D. (2014). Trait Dominance Promotes Reflexive Staring at Masked Angry Body Postures. PloS one, 9(12), e116232. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116232
Hortensius, R., van Honk, J., de Gelder, B., & Terburg, D. (2014). Trait Dominance Promotes Reflexive Staring at Masked Angry Body Postures. PloS one, 9(12), e116232. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116232
 Van den Stock, J., & de Gelder, B. (2014). Face identity matching is influenced by emotions conveyed by face and body. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 8, 53. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00053
Van den Stock, J., & de Gelder, B. (2014). Face identity matching is influenced by emotions conveyed by face and body. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 8, 53. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00053
 Ross, P. D., de Gelder, B., Crabbe, F., & Grosbras, M. H. (2014). Body-selective areas in the visual cortex are less active in children than in adults. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 941. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00941
Ross, P. D., de Gelder, B., Crabbe, F., & Grosbras, M. H. (2014). Body-selective areas in the visual cortex are less active in children than in adults. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 941. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00941
 Costa, T., Cauda, F., Crini, M., Tatu, M-K., Celeghin, A., de Gelder, B., Tamietto, M. (2014). Temporal and spatial neural dynamics in the perception of basic emotions from complex scenes. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 9(11),1690-1703. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nst164
Costa, T., Cauda, F., Crini, M., Tatu, M-K., Celeghin, A., de Gelder, B., Tamietto, M. (2014). Temporal and spatial neural dynamics in the perception of basic emotions from complex scenes. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 9(11),1690-1703. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nst164
 Huis in ‘t Veld, E. M., Van Boxtel, G. J., & de Gelder, B. (2014). The Body Action Coding System II: muscle activations during the perception and expression of emotion. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 8,330. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00330
Huis in ‘t Veld, E. M., Van Boxtel, G. J., & de Gelder, B. (2014). The Body Action Coding System II: muscle activations during the perception and expression of emotion. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 8,330. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00330
 Huis in ‘t Veld, E. M., Van Boxtel, G. J., & de Gelder, B. (2014). The Body Action Coding System I: Muscle activations during the perception and expression of emotion. Social neuroscience, 9(3), 249-264. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2014.890668
Huis in ‘t Veld, E. M., Van Boxtel, G. J., & de Gelder, B. (2014). The Body Action Coding System I: Muscle activations during the perception and expression of emotion. Social neuroscience, 9(3), 249-264. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2014.890668
 Hortensius, R., & de Gelder, B. (2014). The neural basis of the bystander effect—The influence of group size on neural activity when witnessing an emergency. NeuroImage, 93, 53-58. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.02.025
Hortensius, R., & de Gelder, B. (2014). The neural basis of the bystander effect—The influence of group size on neural activity when witnessing an emergency. NeuroImage, 93, 53-58. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.02.025
 Seirafi, M., De Weerd, P., & de Gelder, B. (2014). Suppression of Face Perception during Saccadic Eye Movements. Journal of Ophthalmology, 2014, 384510. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/384510
Seirafi, M., De Weerd, P., & de Gelder, B. (2014). Suppression of Face Perception during Saccadic Eye Movements. Journal of Ophthalmology, 2014, 384510. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/384510
 Van den Stock, J., Tamietto, M., Zhan, M., Heinecke, A., Hervais-Adelman, A. G., Legrand, L., Pegna, A., & de Gelder, B. (2014). Neural Correlates of Body and Face Perception Following Bilateral Destruction of the Primary Visual Cortices. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 8, 30. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00030
Van den Stock, J., Tamietto, M., Zhan, M., Heinecke, A., Hervais-Adelman, A. G., Legrand, L., Pegna, A., & de Gelder, B. (2014). Neural Correlates of Body and Face Perception Following Bilateral Destruction of the Primary Visual Cortices. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 8, 30. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00030
 de Gelder, B., Terburg, D., Morgan, B., Hortensius, R., Stein, D. J., & van Honk, J. (2014). The role of human basolateral amygdala in ambiguous social threat perception. Cortex, 52, 28-34 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2013.12.010
de Gelder, B., Terburg, D., Morgan, B., Hortensius, R., Stein, D. J., & van Honk, J. (2014). The role of human basolateral amygdala in ambiguous social threat perception. Cortex, 52, 28-34 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2013.12.010
 Van den Stock, J., Vandenbulcke, M., Sinke, C.B.A., & Gelder, B. D. (2014). Affective scenes influence fear perception of individual body expressions. Human brain mapping, 35, 492–502. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22195
Van den Stock, J., Vandenbulcke, M., Sinke, C.B.A., & Gelder, B. D. (2014). Affective scenes influence fear perception of individual body expressions. Human brain mapping, 35, 492–502. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22195
Chapter
 de Gelder, B. & Hortensius, R. (2014). The many faces of the emotional body. In Decety, J., & Christen, Y. (Eds.), New Frontiers in Social Neuroscience (pp.153-164). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-02904-7_9
de Gelder, B. & Hortensius, R. (2014). The many faces of the emotional body. In Decety, J., & Christen, Y. (Eds.), New Frontiers in Social Neuroscience (pp.153-164). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-02904-7_9
2013
 Takagi, S., Tabei, K., Huis in 't Veld, E. M., de Gelder, B., & Tanaka, A. (2013). Assessment of incongruent emotions in face and voice. The Japanese Journal of Psychonomic Science. 32(1): 29-39. 高木幸子, 田部井賢一, Huis in ‘t Veld, E. M., de Gelder, B., & 田中章浩. (2013). 表情と音声の示す感情が一致していない刺激からの感情知覚: 異文化間バーチャル・リアリティ・コミュニケーションへの応用 (< 特集> 基礎心理学の実用, 応用展開). 基礎心理学研究, 32(1), 29-39. https://doi.org/10.14947/psychono.kj00008988953
Takagi, S., Tabei, K., Huis in 't Veld, E. M., de Gelder, B., & Tanaka, A. (2013). Assessment of incongruent emotions in face and voice. The Japanese Journal of Psychonomic Science. 32(1): 29-39. 高木幸子, 田部井賢一, Huis in ‘t Veld, E. M., de Gelder, B., & 田中章浩. (2013). 表情と音声の示す感情が一致していない刺激からの感情知覚: 異文化間バーチャル・リアリティ・コミュニケーションへの応用 (< 特集> 基礎心理学の実用, 応用展開). 基礎心理学研究, 32(1), 29-39. https://doi.org/10.14947/psychono.kj00008988953
 Kret, M. E., & de Gelder, B. (2013). When a smile becomes a fist: the perception of facial and bodily expressions of emotion in violent offenders. Experimental brain research, 228(4), 399-410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3557-6
Kret, M. E., & de Gelder, B. (2013). When a smile becomes a fist: the perception of facial and bodily expressions of emotion in violent offenders. Experimental brain research, 228(4), 399-410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3557-6
 Del Zotto, M., Deiber, M. P., Legrand, L. B., De Gelder, B., & Pegna, A. J. (2013). Emotional expressions modulate low α and β oscillations in a cortically blind patient. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 90(3), 358-62.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2013.10.007
Del Zotto, M., Deiber, M. P., Legrand, L. B., De Gelder, B., & Pegna, A. J. (2013). Emotional expressions modulate low α and β oscillations in a cortically blind patient. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 90(3), 358-62.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2013.10.007
 Burra, N., Hervais-Adelman, A., Kerzel, D., Tamietto, M., De Gelder, B., & Pegna, A. J. (2013). Amygdala Activation for Eye Contact Despite Complete Cortical Blindness. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(25), 10483-10489. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3994-12.2013
Burra, N., Hervais-Adelman, A., Kerzel, D., Tamietto, M., De Gelder, B., & Pegna, A. J. (2013). Amygdala Activation for Eye Contact Despite Complete Cortical Blindness. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(25), 10483-10489. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3994-12.2013
 Kret, M.E., Roelofs, K., Stekelenburg, J., & de Gelder, B. (2013). Emotional signals from faces, bodies and scenes influence observers' face expressions, fixations and pupil-size. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 810. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00810
Kret, M.E., Roelofs, K., Stekelenburg, J., & de Gelder, B. (2013). Emotional signals from faces, bodies and scenes influence observers' face expressions, fixations and pupil-size. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 810. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00810
 Van den Stock, J., Vandenbulcke, M., Sinke, C., Goebel, R., & de Gelder, B. (2013). How affective information from faces and scenes interacts in the brain. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 9(10), 1481-8. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nst138
Van den Stock, J., Vandenbulcke, M., Sinke, C., Goebel, R., & de Gelder, B. (2013). How affective information from faces and scenes interacts in the brain. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 9(10), 1481-8. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nst138
 Van den Stock, J., de Gelder, B., Van Laere, K. & Vandenbulcke, M. (2013). Face-selective hyper-animacy and hyper-familiarity misperception in a patient with moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 25(4), E52-E53. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.neuropsych.12120390
Van den Stock, J., de Gelder, B., Van Laere, K. & Vandenbulcke, M. (2013). Face-selective hyper-animacy and hyper-familiarity misperception in a patient with moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 25(4), E52-E53. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.neuropsych.12120390
 Meeren, H.K.M., de Gelder, B., Ahlfors, S.P., Hämäläinen, M.S., Hadjikhani, N. (2013). Different Cortical Dynamics in Face and Body Perception: An MEG study. PLoS ONE 8(9), e71408. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071408
Meeren, H.K.M., de Gelder, B., Ahlfors, S.P., Hämäläinen, M.S., Hadjikhani, N. (2013). Different Cortical Dynamics in Face and Body Perception: An MEG study. PLoS ONE 8(9), e71408. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071408
![]() Seirafi, M., De Weerd, P. & de Gelder, B. (2013). Emotion categorization does not depend on explicit face categorization. Journal of Vision, 13, 12. https://doi.org/10.1167/13.2.12
Seirafi, M., De Weerd, P. & de Gelder, B. (2013). Emotion categorization does not depend on explicit face categorization. Journal of Vision, 13, 12. https://doi.org/10.1167/13.2.12
 Kret, M.E., Stekelenburg, J.J., Roelofs, K. & de Gelder B. (2013). Perception of face and body expressions using electromyography, pupillometry and gaze measures. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 28. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00028
Kret, M.E., Stekelenburg, J.J., Roelofs, K. & de Gelder B. (2013). Perception of face and body expressions using electromyography, pupillometry and gaze measures. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 28. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00028
 de Jong J.S., de Gelder B. & Hodiamont, P.P. (2013). Sensory processing, neurocognition, and social cognition in schizophrenia: Towards a cohesive cognitive model. Schizophrenia Research, 146, 209-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2013.02.034
de Jong J.S., de Gelder B. & Hodiamont, P.P. (2013). Sensory processing, neurocognition, and social cognition in schizophrenia: Towards a cohesive cognitive model. Schizophrenia Research, 146, 209-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2013.02.034
 Kristo, G., Leemans, A., de Gelder, B., Raemaekers, M., Rutten, G. J., & Ramsey, N. (2013). Reliability of the corticospinal tract and arcuate fasciculus reconstructed with DTI-based tractography: implications for clinical practice. European radiology, 23(1), 28-36.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2589-9
Kristo, G., Leemans, A., de Gelder, B., Raemaekers, M., Rutten, G. J., & Ramsey, N. (2013). Reliability of the corticospinal tract and arcuate fasciculus reconstructed with DTI-based tractography: implications for clinical practice. European radiology, 23(1), 28-36.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2589-9
 Buetti, S., Tamietto, M., Hervais-Adelman, A., Kerzel, D., De Gelder, B., & Pegna, A. J. (2013). Dissociation between goal-directed and discrete response localization in a patient with bilateral cortical blindness. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 25(10), 1769-1775. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00404
Buetti, S., Tamietto, M., Hervais-Adelman, A., Kerzel, D., De Gelder, B., & Pegna, A. J. (2013). Dissociation between goal-directed and discrete response localization in a patient with bilateral cortical blindness. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 25(10), 1769-1775. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00404
 Zhu, Q., Nelissen, K., Van den Stock, J., De Winter, F. L., Pauwels, K., de Gelder, B., ... & Vandenbulcke, M. (2013). Dissimilar processing of emotional facial expressions in human and monkey temporal cortex. Neuroimage, 66, 402-411. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.10.083
Zhu, Q., Nelissen, K., Van den Stock, J., De Winter, F. L., Pauwels, K., de Gelder, B., ... & Vandenbulcke, M. (2013). Dissimilar processing of emotional facial expressions in human and monkey temporal cortex. Neuroimage, 66, 402-411. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.10.083
2012
 Huis in 't Veld, E.M.J., Van den Stock, J., & de Gelder, B. (2012). Configuration perception, face memory and face context effects in developmental prosopagnosia. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 29 (5 –6), 464-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/02643294.2012.732051
Huis in 't Veld, E.M.J., Van den Stock, J., & de Gelder, B. (2012). Configuration perception, face memory and face context effects in developmental prosopagnosia. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 29 (5 –6), 464-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/02643294.2012.732051
 Ioannides, A.A., Poghosyan, V., Liu, L., Saridis, G.A., Tamietto, M., Op de Beeck, M., De Tiège, X., Weiskrantz, L. & de Gelder B. (2012). Spatiotemporal profiles of visual processing with and without primary visual cortex, NeuroImage, 63(3), 1464-77. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.07.058
Ioannides, A.A., Poghosyan, V., Liu, L., Saridis, G.A., Tamietto, M., Op de Beeck, M., De Tiège, X., Weiskrantz, L. & de Gelder B. (2012). Spatiotemporal profiles of visual processing with and without primary visual cortex, NeuroImage, 63(3), 1464-77. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.07.058
 Tamietto, M., Pullens, P., de Gelder, B., Weiskrantz, L. & Goebel, R. (2012). Subcortical connections to human amygdala and their changes following destruction of the visual cortex. Current Biology, 22(15), 1449-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.06.006
Tamietto, M., Pullens, P., de Gelder, B., Weiskrantz, L. & Goebel, R. (2012). Subcortical connections to human amygdala and their changes following destruction of the visual cortex. Current Biology, 22(15), 1449-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.06.006
 de Gelder, B., Hortensius, R, & Tamietto, M. (2012). Attention and awareness influence amygdala activity for dynamic bodily expressions - A short review. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 6, 54. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2012.00054
de Gelder, B., Hortensius, R, & Tamietto, M. (2012). Attention and awareness influence amygdala activity for dynamic bodily expressions - A short review. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 6, 54. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2012.00054
 Van den Stock, J., de Gelder, B., De Winter, F-L., Van Laere, K., & Vandenbulcke, M. (2012). A strange face in the mirror. Face-selective misindentification in a patient with right lateralized occipito-temporal hypo-metabolism. Cortex, 48(8), 1088-903. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2012.03.003.
Van den Stock, J., de Gelder, B., De Winter, F-L., Van Laere, K., & Vandenbulcke, M. (2012). A strange face in the mirror. Face-selective misindentification in a patient with right lateralized occipito-temporal hypo-metabolism. Cortex, 48(8), 1088-903. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2012.03.003.
 Sinke, C. B. A., Van den Stock, J., Goebel, R. & de Gelder, B. (2012). The constructive nature of affective vision: seeing fearful scenes activates extrastriate body area. Plos One, 7(6), e38118. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038118
Sinke, C. B. A., Van den Stock, J., Goebel, R. & de Gelder, B. (2012). The constructive nature of affective vision: seeing fearful scenes activates extrastriate body area. Plos One, 7(6), e38118. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038118
 Stienen, B. M. C., Schindler, K. & de Gelder, B. (2012). A computational feed-forward model predicts categorization of masked emotional body language for longer, but not for shorter latencies. Neural Computation, 24(7), 1806-21. https://doi.org/10.1162/NECO_a_00305
Stienen, B. M. C., Schindler, K. & de Gelder, B. (2012). A computational feed-forward model predicts categorization of masked emotional body language for longer, but not for shorter latencies. Neural Computation, 24(7), 1806-21. https://doi.org/10.1162/NECO_a_00305
 Van den Stock, J., Vandenbulcke, M., Zhu, Q., Hadjikhani, N. & de Gelder, B. (2012). Developmental prosopagnosia in a patient with hypoplasia of the vermis cerebelli. Neurology, 78(21), 1700-2. doi: https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182575130
Van den Stock, J., Vandenbulcke, M., Zhu, Q., Hadjikhani, N. & de Gelder, B. (2012). Developmental prosopagnosia in a patient with hypoplasia of the vermis cerebelli. Neurology, 78(21), 1700-2. doi: https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182575130
 de Gelder, B. & VandenBulcke, M. (2012). Emotions as mind organs. Behavioral Brain Sciences, 35(3), 147-8. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0140525x11001695
de Gelder, B. & VandenBulcke, M. (2012). Emotions as mind organs. Behavioral Brain Sciences, 35(3), 147-8. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0140525x11001695
 Kret, M. E. & de Gelder, B. (2012). Islamic Headdress Influences How Emotion is Recognized from the Eyes. Frontiers in Emotion Science, 3, 110. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00110
Kret, M. E. & de Gelder, B. (2012). Islamic Headdress Influences How Emotion is Recognized from the Eyes. Frontiers in Emotion Science, 3, 110. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00110
 Pichon, S., de Gelder, B., & Grèzes, J. (2012). Threat prompts defensive brain responses independently of attentional control. Cerebral Cortex, 22 (2), 274-85. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhr060
Pichon, S., de Gelder, B., & Grèzes, J. (2012). Threat prompts defensive brain responses independently of attentional control. Cerebral Cortex, 22 (2), 274-85. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhr060
 Frissen, I., Vroomen, J. & de Gelder, B. (2012).The aftereffects of ventrioloquism: The time course of the visual recalibration of auditory localization. Seeing and perceiving, 25(1), 1-14. doi: 10.1163/187847611X620883.
Frissen, I., Vroomen, J. & de Gelder, B. (2012).The aftereffects of ventrioloquism: The time course of the visual recalibration of auditory localization. Seeing and perceiving, 25(1), 1-14. doi: 10.1163/187847611X620883.
 Kret, M. E. & de Gelder, B. (2012). A review on sex differences in processing emotional signals. Neuropsychologia, 50(7), 1211-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.12.022
Kret, M. E. & de Gelder, B. (2012). A review on sex differences in processing emotional signals. Neuropsychologia, 50(7), 1211-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.12.022
 Van den Stock, J. & de Gelder, B. (2012). Emotional information in body and background hampers recognition memory for faces. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 97(3), 321-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2012.01.007
Van den Stock, J. & de Gelder, B. (2012). Emotional information in body and background hampers recognition memory for faces. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 97(3), 321-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2012.01.007
Chapters
 de Gelder, B., & Van den Stock, J. (2012). Real faces, real emotions: perceiving facial expressions in naturalistic contexts of voices, bodies and scenes. In A.J. Calder, G. Rhodes, J.V. Haxby & M.H. Johnson (Eds.), The handbook of face perception. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
de Gelder, B., & Van den Stock, J. (2012). Real faces, real emotions: perceiving facial expressions in naturalistic contexts of voices, bodies and scenes. In A.J. Calder, G. Rhodes, J.V. Haxby & M.H. Johnson (Eds.), The handbook of face perception. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
 de Gelder, B. (2012). From body perception to action preparation. A distributed neural system for viewing bodily expressions of emotion. In K. L. Johnson & M. Shiffrar (Eds.), Visual perception of the human body in motion. Findings, theory and practice. New York: Oxford University Press.
de Gelder, B. (2012). From body perception to action preparation. A distributed neural system for viewing bodily expressions of emotion. In K. L. Johnson & M. Shiffrar (Eds.), Visual perception of the human body in motion. Findings, theory and practice. New York: Oxford University Press.
 Giese, M.A., & de Gelder, B. (2012). Nichtverbale Kommunikation. In H-O. Karnath & Thier, P. (Eds), Kognitive Neurowissenschaften. Springer-Lehrbuch. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25527-4
Giese, M.A., & de Gelder, B. (2012). Nichtverbale Kommunikation. In H-O. Karnath & Thier, P. (Eds), Kognitive Neurowissenschaften. Springer-Lehrbuch. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25527-4
2011
 Stienen, B. M. C. & de Gelder, B. (2011). Fear modulates visual awareness similary for facial and bodily expressions. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 5, 132. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2011.00132
Stienen, B. M. C. & de Gelder, B. (2011). Fear modulates visual awareness similary for facial and bodily expressions. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 5, 132. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2011.00132
 Koizumi, A., Tanaka, A., Imai, H., Hiramatsu, S., Hiramoto, E., Sato, T., & de Gelder, B. (2011). The effects of anxiety on the interpretation of emotion in the face-voice pairs. Experimental Brain Research, 213 (2-3), 275-82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-011-2668-1
Koizumi, A., Tanaka, A., Imai, H., Hiramatsu, S., Hiramoto, E., Sato, T., & de Gelder, B. (2011). The effects of anxiety on the interpretation of emotion in the face-voice pairs. Experimental Brain Research, 213 (2-3), 275-82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-011-2668-1
 Candidi, M., Stienen, B. M. C., Aglioti, S. M., & de Gelder, B. (2011). Event-related repetitive TMS of posterior Superior Temporal Sulcus improves the detection of threatening human body postural changes. Journal of Neuroscience, 31 (48), 17547-55. doi: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0697-11.2011
Candidi, M., Stienen, B. M. C., Aglioti, S. M., & de Gelder, B. (2011). Event-related repetitive TMS of posterior Superior Temporal Sulcus improves the detection of threatening human body postural changes. Journal of Neuroscience, 31 (48), 17547-55. doi: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0697-11.2011
 Van den Stock, J., de Jong, J.J., Hodiamont, P.P.G., & de Gelder, B. (2011). Perceiving emotions from bodily expressions and multisensory integration of emotion cues in schizophrenia. Social Neuroscience, 6 (5–6), 537–547. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2011.568790
Van den Stock, J., de Jong, J.J., Hodiamont, P.P.G., & de Gelder, B. (2011). Perceiving emotions from bodily expressions and multisensory integration of emotion cues in schizophrenia. Social Neuroscience, 6 (5–6), 537–547. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2011.568790
 Stienen, B. M. C., Tanaka, A., & de Gelder, B. (2011). Emotional Voice and Emotional Body Postures Influence Each Other Independently of Visual Awareness. PLoS ONE, 6(10), e25517. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025517
Stienen, B. M. C., Tanaka, A., & de Gelder, B. (2011). Emotional Voice and Emotional Body Postures Influence Each Other Independently of Visual Awareness. PLoS ONE, 6(10), e25517. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025517
 Stienen, B.M.C. & de Gelder, B. (2011). Fear detection and visual awareness in perceiving bodily expressions. Emotion, 11(5), 1182-89. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/a0024032
Stienen, B.M.C. & de Gelder, B. (2011). Fear detection and visual awareness in perceiving bodily expressions. Emotion, 11(5), 1182-89. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/a0024032
 Van den Stock, J., Tamietto, M., Sorger, B., Pichon, S., Grèzes & de Gelder, B. (2011). Cortico-subcortical visual, somatosensory and motor activations for perceiving dynamic whole-body emotional expressions with and without V1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 108(39), 16188-193. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1107214108
Van den Stock, J., Tamietto, M., Sorger, B., Pichon, S., Grèzes & de Gelder, B. (2011). Cortico-subcortical visual, somatosensory and motor activations for perceiving dynamic whole-body emotional expressions with and without V1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 108(39), 16188-193. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1107214108
 Magnee, M. J., de Gelder, B., van Engeland, H., & Kemner, C. (2011). Multisensory integration and attention in autism spectrum disorder: Evidence from event-related potentials. PLoS One, 6(8), e24196. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024196
Magnee, M. J., de Gelder, B., van Engeland, H., & Kemner, C. (2011). Multisensory integration and attention in autism spectrum disorder: Evidence from event-related potentials. PLoS One, 6(8), e24196. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024196
 de Gelder, B. & Van den Stock, J. (2011). The Bodily Expressive Action Stimulus Test (BEAST). Construction and validation of a stimulus basis for measuring perception of whole body expression of emotions. Frontiers in Psychology, 2, 181. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00181
de Gelder, B. & Van den Stock, J. (2011). The Bodily Expressive Action Stimulus Test (BEAST). Construction and validation of a stimulus basis for measuring perception of whole body expression of emotions. Frontiers in Psychology, 2, 181. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00181
Click here for BEAST stimuli and validation data.
 de Gelder, B., van Honk, J. & Tamietto, M. (2011). Emotion in the brain: of low roads, high roads and roads less travelled. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(7),425. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2920-c1
de Gelder, B., van Honk, J. & Tamietto, M. (2011). Emotion in the brain: of low roads, high roads and roads less travelled. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(7),425. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2920-c1
 de Gelder, B. & Tamietto, M. (2011). A unified science of the non-conscious mind? Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12,302. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2889-c2
de Gelder, B. & Tamietto, M. (2011). A unified science of the non-conscious mind? Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12,302. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2889-c2
 Held, R., Ostrovsky, Y., de Gelder, B., Gandhi, T., Ganesh, S., Mathur, U., & Sinha, P. (2011). The newly sighted fail to match seen with felt. Nature Neuroscience,14(5),551-3. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2795
Held, R., Ostrovsky, Y., de Gelder, B., Gandhi, T., Ganesh, S., Mathur, U., & Sinha, P. (2011). The newly sighted fail to match seen with felt. Nature Neuroscience,14(5),551-3. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2795
 Tamietto, M., & de Gelder, B. (2011). Sentinels in the visual system. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 5, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00006
Tamietto, M., & de Gelder, B. (2011). Sentinels in the visual system. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 5, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00006
 Kret, M.E., Pichon, S., Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2011). Men fear other men most: Gender specific brain activations in perceiving threat from dynamic faces and bodies. An fMRI study. Frontiers in Emotion Science, 2, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00003
Kret, M.E., Pichon, S., Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2011). Men fear other men most: Gender specific brain activations in perceiving threat from dynamic faces and bodies. An fMRI study. Frontiers in Emotion Science, 2, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00003
 Kret, M.E., Denollet, J., Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2011). The role of negative affectivity and social inhibition in perceiving social threat: an fMRI study. Neuropsychologia, 5, 1187-1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.02.007
Kret, M.E., Denollet, J., Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2011). The role of negative affectivity and social inhibition in perceiving social threat: an fMRI study. Neuropsychologia, 5, 1187-1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.02.007
2010
 Kret ME, Pichon S, Grèzes J, de Gelder B. Similarities and differences in perceiving threat from dynamic faces and bodies. An fMRI study. Neuroimage, 54, 1755-1762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.08.012
Kret ME, Pichon S, Grèzes J, de Gelder B. Similarities and differences in perceiving threat from dynamic faces and bodies. An fMRI study. Neuroimage, 54, 1755-1762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.08.012
 Gelder, B. D. (2010). The grand challenge for frontiers in emotion science. Frontiers in psychology, 1, 187. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2010.00187
Gelder, B. D. (2010). The grand challenge for frontiers in emotion science. Frontiers in psychology, 1, 187. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2010.00187
 de Jong, J.J., Hodiamont, P.P.G., de Gelder, B. (2010). Modality-specific attention and multisensory integration of emotions in schizophrenia: Reduced regulatory effects. Schizophrenia Research, 122, 136-143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2010.04.010
de Jong, J.J., Hodiamont, P.P.G., de Gelder, B. (2010). Modality-specific attention and multisensory integration of emotions in schizophrenia: Reduced regulatory effects. Schizophrenia Research, 122, 136-143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2010.04.010
 Tamietto, M., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Neural bases of the non-conscious perception of emotional signals. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 11, 697 - 709. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2889
Tamietto, M., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Neural bases of the non-conscious perception of emotional signals. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 11, 697 - 709. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2889
 Tanaka, A., Koizumi, A., Imai, H., Hiramatsu, S., Hiramoto, E., & de Gelder, B. (2010). I feel your voice: Cultural differences in the multisensory perception of emotion. Psychological Science, 21(9),1259-1262. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797610380698
Tanaka, A., Koizumi, A., Imai, H., Hiramatsu, S., Hiramoto, E., & de Gelder, B. (2010). I feel your voice: Cultural differences in the multisensory perception of emotion. Psychological Science, 21(9),1259-1262. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797610380698
 Pouga, L., Berthoz, S., de Gelder, B., & Grèzes, J. (2010). Individual differences in socioaffective skills influence the neural bases of fear processing: The case of alexithymia. Human Brain Mapping, 31(10), 1469–1481. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20953
Pouga, L., Berthoz, S., de Gelder, B., & Grèzes, J. (2010). Individual differences in socioaffective skills influence the neural bases of fear processing: The case of alexithymia. Human Brain Mapping, 31(10), 1469–1481. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20953
 de Gelder, B. (2010). Uncanny Sight in the Blind. Scientific American, 302, 60-65. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26002034
de Gelder, B. (2010). Uncanny Sight in the Blind. Scientific American, 302, 60-65. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26002034
 Kret, M.E., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Social context influences recognition of bodily expressions.Experimental Brain Research 203(1), 169-180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-010-2220-8
Kret, M.E., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Social context influences recognition of bodily expressions.Experimental Brain Research 203(1), 169-180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-010-2220-8
 de Gelder, B., Van den Stock, J., Meeren, H.K.M., Sinke, C.B.A., Kret, M.E., & Tamietto, M. (2010). Standing up for the body. Recent progress in uncovering the networks involved in processing bodies and bodily expressions. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 34(4), 513-527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.10.008
de Gelder, B., Van den Stock, J., Meeren, H.K.M., Sinke, C.B.A., Kret, M.E., & Tamietto, M. (2010). Standing up for the body. Recent progress in uncovering the networks involved in processing bodies and bodily expressions. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 34(4), 513-527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.10.008
 Tamietto, M., Cauda, F., Corazzini, L.L., Savazzi, S., Marzi, C.A., Goebel, R., Weiskrantz, W., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Collicular vision guides non-conscious behavior. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22(5), 888-902. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2009.21225
Tamietto, M., Cauda, F., Corazzini, L.L., Savazzi, S., Marzi, C.A., Goebel, R., Weiskrantz, W., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Collicular vision guides non-conscious behavior. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22(5), 888-902. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2009.21225
 Sinke, C.B.A., Sorger, B., Goebel, R., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Tease or threat? Judging social interactions from bodily expressions. NeuroImage, 49(2), 1717-1727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.065
Sinke, C.B.A., Sorger, B., Goebel, R., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Tease or threat? Judging social interactions from bodily expressions. NeuroImage, 49(2), 1717-1727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.065
Chapters
 Sinke, C.B.A., Kret, M.E., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Body language: embodied perception of emotion. In B. Berglund, G.B. Rossi, J.T. Townsend & L.R. Pendrill (Eds.), Measuring with persons: theory, methods and implementation areas. Psychology Press/ Taylor & Francis.
Sinke, C.B.A., Kret, M.E., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Body language: embodied perception of emotion. In B. Berglund, G.B. Rossi, J.T. Townsend & L.R. Pendrill (Eds.), Measuring with persons: theory, methods and implementation areas. Psychology Press/ Taylor & Francis.
 Kret, M.E., Sinke, C.B.A., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Emotion perception and health. In I. Nyklicek, A.J.J.M. Vingerhoets & M. Zeelenberg (Eds), Emotion regulation and well-being. New York: Springer.
Kret, M.E., Sinke, C.B.A., & de Gelder, B. (2010). Emotion perception and health. In I. Nyklicek, A.J.J.M. Vingerhoets & M. Zeelenberg (Eds), Emotion regulation and well-being. New York: Springer.
 de Gelder, B., & Van den Stock, J. (2010). Moving and being moved. The relative importance of dynamical information for residual face processing in clinical populations and brain damaged patients. In C. Curio, H.H. Bülthoff & M.A. Giese (Eds.), Dynamic faces: Insights from experiments and computation. MIT Press.
de Gelder, B., & Van den Stock, J. (2010). Moving and being moved. The relative importance of dynamical information for residual face processing in clinical populations and brain damaged patients. In C. Curio, H.H. Bülthoff & M.A. Giese (Eds.), Dynamic faces: Insights from experiments and computation. MIT Press.
 de Gelder, B., & Tamietto, M. (2010). Faces, bodies, agent vision and social consciousness. In B.A. Adams, N. Ambady, K. Nakayama & S. Shimojo (Eds.), The science of social vision. New York: Oxford University Press.
de Gelder, B., & Tamietto, M. (2010). Faces, bodies, agent vision and social consciousness. In B.A. Adams, N. Ambady, K. Nakayama & S. Shimojo (Eds.), The science of social vision. New York: Oxford University Press.
2009
 de Gelder, B., & Bertelson, P. (2009). A comparative approach to testing face perception: Face and object identification by adults in a simultaneous matching task. Psychologica Belgica, 42(2&3), 177-190.
de Gelder, B., & Bertelson, P. (2009). A comparative approach to testing face perception: Face and object identification by adults in a simultaneous matching task. Psychologica Belgica, 42(2&3), 177-190.
 de Gelder, B. (2009). Why bodies? Twelve reasons for including bodily expressions in affective neuroscience. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 364(1535), 3475-3484. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0190
de Gelder, B. (2009). Why bodies? Twelve reasons for including bodily expressions in affective neuroscience. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 364(1535), 3475-3484. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0190
 Tamietto, M., Castelli, L., Vighetti, S., Perozzo, P., Geminiani, G., Weiskrantz, L., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Unseen facial and bodily expressions trigger fast emotional reactions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 106(42), 17661-17666. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0908994106
Tamietto, M., Castelli, L., Vighetti, S., Perozzo, P., Geminiani, G., Weiskrantz, L., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Unseen facial and bodily expressions trigger fast emotional reactions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 106(42), 17661-17666. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0908994106
 Van den Stock, J., Peretz, I., Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Instrumental music influences recognition of emotional body language. Brain Topography, 21(3-4), 216-220. Instrumental Music Influences Recognition of Emotional Body
Language
Van den Stock, J., Peretz, I., Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Instrumental music influences recognition of emotional body language. Brain Topography, 21(3-4), 216-220. Instrumental Music Influences Recognition of Emotional Body
Language
 Pichon, S., de Gelder, B., & Grezes, J. (2009). Two different faces of threat. Comparing the neural systems for recognizing fear and anger in dynamic body expressions. Neuroimage, 47(4), 1873-1883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.03.084
Pichon, S., de Gelder, B., & Grezes, J. (2009). Two different faces of threat. Comparing the neural systems for recognizing fear and anger in dynamic body expressions. Neuroimage, 47(4), 1873-1883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.03.084
 Grezes, J., Wicker, B., Berthoz, S., & de Gelder, B. (2009). A failure to grasp the affective meaning of actions in autism spectrum disorder subjects. Neuropsychologia, 47(8-9), 1816-1825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.02.021
Grezes, J., Wicker, B., Berthoz, S., & de Gelder, B. (2009). A failure to grasp the affective meaning of actions in autism spectrum disorder subjects. Neuropsychologia, 47(8-9), 1816-1825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.02.021
 de Gelder, B., & Partan, S. (2009). The neural basis of perceiving emotional bodily expressions in monkeys. Neuroreport, 20(7), 642-646. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32832a1e56
de Gelder, B., & Partan, S. (2009). The neural basis of perceiving emotional bodily expressions in monkeys. Neuroreport, 20(7), 642-646. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32832a1e56
 de Jong, J.J., Hodiamont, P.P.G. , Van den Stock, J., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Audiovisual emotion recognition in schizophrenia: Reduced integration of facial and vocal affect. Schizophrenia Research, 107(2-3),286-293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2008.10.001
de Jong, J.J., Hodiamont, P.P.G. , Van den Stock, J., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Audiovisual emotion recognition in schizophrenia: Reduced integration of facial and vocal affect. Schizophrenia Research, 107(2-3),286-293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2008.10.001
 Bannerman, R.L., Milders, M., de Gelder, B., & Sahraie, A. (2009). Orienting to threat: Faster localization of fearful facial expressions and body postures revealed by saccadic eye movements.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B, 276(1662),1635-1641. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2008.1744
Bannerman, R.L., Milders, M., de Gelder, B., & Sahraie, A. (2009). Orienting to threat: Faster localization of fearful facial expressions and body postures revealed by saccadic eye movements.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B, 276(1662),1635-1641. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2008.1744
 Hadjikhani, N., Joseph, R.M., Manoach, D.S., Naik, P., Snyder, N., Dominick, K., Hoge, R., Van den Stock, J., Flusberg, H.T., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Body expressions of emotion do not trigger fear contagion in autism spectrum disorder. Social, Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 4(1),70-78. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsn038
Hadjikhani, N., Joseph, R.M., Manoach, D.S., Naik, P., Snyder, N., Dominick, K., Hoge, R., Van den Stock, J., Flusberg, H.T., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Body expressions of emotion do not trigger fear contagion in autism spectrum disorder. Social, Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 4(1),70-78. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsn038
 Tamietto, M., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Emotional contagion for unseen bodily expressions: Evidence from facial EMG. Proceeding of the FG 2008 meeting, Amsterdam. DOI: 10.1109/AFGR.2008.4813317
Tamietto, M., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Emotional contagion for unseen bodily expressions: Evidence from facial EMG. Proceeding of the FG 2008 meeting, Amsterdam. DOI: 10.1109/AFGR.2008.4813317
 van de Riet, W.A.C., Grèzes , J., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Specific and common brain regions involved in the perception of faces and bodies and the representation of their emotional expressions. Social Neuroscience, 4(2), 101-120. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17470910701865367
van de Riet, W.A.C., Grèzes , J., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Specific and common brain regions involved in the perception of faces and bodies and the representation of their emotional expressions. Social Neuroscience, 4(2), 101-120. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17470910701865367
2008
 van de Riet, W. A., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Watch the face and look at the body!. Netherlands Journal of Psychology, 64(4), 143-151. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03076417
van de Riet, W. A., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Watch the face and look at the body!. Netherlands Journal of Psychology, 64(4), 143-151. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03076417
 Vroomen, J. & de Gelder, B. (2009). In Memory of Paul Bertelson (1926–2008). Brain Topogr, 21, 155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-009-0100-y
Vroomen, J. & de Gelder, B. (2009). In Memory of Paul Bertelson (1926–2008). Brain Topogr, 21, 155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-009-0100-y
 Righart, R. & de Gelder, B., (2008). Rapid influence of emotional scenes on encoding of facial expressions. An ERP study. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 3, 270-278. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsn021
Righart, R. & de Gelder, B., (2008). Rapid influence of emotional scenes on encoding of facial expressions. An ERP study. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 3, 270-278. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsn021
 Hadjikhani, N., Hoge, R., Snyder, J. , & de Gelder, B. (2008). Pointing with the eyes: The role of gaze in communicating danger. Brain and Cognition, 68(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2008.01.008
Hadjikhani, N., Hoge, R., Snyder, J. , & de Gelder, B. (2008). Pointing with the eyes: The role of gaze in communicating danger. Brain and Cognition, 68(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2008.01.008
 Tamietto, M. & de Gelder, B. (2008). Affective blindsight in the intact brain: Neural interhemispheric summation for unseen fearful expressions. Neuropsychologia, 46(3), 820-828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.11.002
Tamietto, M. & de Gelder, B. (2008). Affective blindsight in the intact brain: Neural interhemispheric summation for unseen fearful expressions. Neuropsychologia, 46(3), 820-828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.11.002
 de Gelder, B., Van den Stock, J., de Diego Balaguer, R., & Bachoud-Lévi, A.-C.(2008). Huntington's disease impairs recognition of angry and instrumental body language. Neuropsychologia, 46,369-373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.10.015
de Gelder, B., Van den Stock, J., de Diego Balaguer, R., & Bachoud-Lévi, A.-C.(2008). Huntington's disease impairs recognition of angry and instrumental body language. Neuropsychologia, 46,369-373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.10.015
 Van den Stock, J., Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Human and animal sounds influence recognition of body language. Brain Research, 1242, 185-190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.05.040
Van den Stock, J., Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Human and animal sounds influence recognition of body language. Brain Research, 1242, 185-190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.05.040
 de Gelder, B., Tamietto, M., van Boxtel, G., Goebel, R., Sahraie, A., Van den Stock, J., Stienen, B. M. C., Weiskrantz, L., & Pegna, A. (2008). Intact navigation skills after bilateral loss of striate cortex.Current Biology, 18(24), R1128-R1129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2008.11.002
de Gelder, B., Tamietto, M., van Boxtel, G., Goebel, R., Sahraie, A., Van den Stock, J., Stienen, B. M. C., Weiskrantz, L., & Pegna, A. (2008). Intact navigation skills after bilateral loss of striate cortex.Current Biology, 18(24), R1128-R1129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2008.11.002
 Meeren, H.K.M., Hadjikhani, N., Ahlfors, S.P., Hämäläinen, M.S., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Early category-specific cortical activation revealed by visual stimulus inversion. PLoS ONE 3(10): e3503. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003503
Meeren, H.K.M., Hadjikhani, N., Ahlfors, S.P., Hämäläinen, M.S., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Early category-specific cortical activation revealed by visual stimulus inversion. PLoS ONE 3(10): e3503. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003503
 Schindler, K., Van Gool, L., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Recognizing emotions expressed by body pose: A biologically inspired neural model. Neural Networks, 21(9),1238-1246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2008.05.003
Schindler, K., Van Gool, L., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Recognizing emotions expressed by body pose: A biologically inspired neural model. Neural Networks, 21(9),1238-1246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2008.05.003
 Van den Stock, J., van de Riet, W.A.C., Righart, R., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Neural correlates of perceiving emotional faces and bodies in developmental prosopagnosia: An event-related fMRI-study. PLoS ONE, 3(9): e3195. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003195
Van den Stock, J., van de Riet, W.A.C., Righart, R., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Neural correlates of perceiving emotional faces and bodies in developmental prosopagnosia: An event-related fMRI-study. PLoS ONE, 3(9): e3195. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003195
 Magnée, M.J.C.M., de Gelder, B., van Engeland, H., & Kemner, C. (2008). Audiovisual speech integration in Pervasive Developmental Disorder: Evidence from event-related potentials. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49(9), 995-1000. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.01902.x
Magnée, M.J.C.M., de Gelder, B., van Engeland, H., & Kemner, C. (2008). Audiovisual speech integration in Pervasive Developmental Disorder: Evidence from event-related potentials. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49(9), 995-1000. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.01902.x
 de Gelder, B., van de Riet, W.A.C., Grèzes, J., & Denollet, J. (2008). Decreased differential activity in the amygdala in response to fearful expressions in Type D personality. Neurophysiologie Clinique/Clinical Neurophysiologie, 38, 163-169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2008.03.002
de Gelder, B., van de Riet, W.A.C., Grèzes, J., & Denollet, J. (2008). Decreased differential activity in the amygdala in response to fearful expressions in Type D personality. Neurophysiologie Clinique/Clinical Neurophysiologie, 38, 163-169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2008.03.002
 Magneé, M.J.C.M., de Gelder, B., van Engeland, H. & Kemner, C. (2008). Atypical processing of fearful face–voice pairs in Pervasive Developmental Disorder: An ERP study. Clinical Neurophysiology, 119, 2004-2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2008.05.005
Magneé, M.J.C.M., de Gelder, B., van Engeland, H. & Kemner, C. (2008). Atypical processing of fearful face–voice pairs in Pervasive Developmental Disorder: An ERP study. Clinical Neurophysiology, 119, 2004-2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2008.05.005
 Denollet, J., Martens, E.J., Nyklicek, I, Conraads, V.M. & de Gelder, B. (2008). Clinical Events in Coronary Patients Who Report Low Distress: Adverse Effect of Repressive Coping. Health Psychology, 27(3), 302-308. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0278-6133.27.3.302
Denollet, J., Martens, E.J., Nyklicek, I, Conraads, V.M. & de Gelder, B. (2008). Clinical Events in Coronary Patients Who Report Low Distress: Adverse Effect of Repressive Coping. Health Psychology, 27(3), 302-308. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0278-6133.27.3.302
 Bannerman, R.L., Milders, M., De Gelder, B., & Sahraie, A. (2008). Influence of emotional facial expressions on binocular rivalry. Ophthalmic & Physiological Optics , 28(4), 317-326. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-1313.2008.00568.x
Bannerman, R.L., Milders, M., De Gelder, B., & Sahraie, A. (2008). Influence of emotional facial expressions on binocular rivalry. Ophthalmic & Physiological Optics , 28(4), 317-326. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-1313.2008.00568.x
 Pichon, S., de Gelder, B., & Grèzes, J. (2008). Emotional modulation of visual and motor areas by dynamic body expressions of anger. Social Neuroscience, 3(3-4), 199-212. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470910701394368
Pichon, S., de Gelder, B., & Grèzes, J. (2008). Emotional modulation of visual and motor areas by dynamic body expressions of anger. Social Neuroscience, 3(3-4), 199-212. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470910701394368
 Righart, R., & De Gelder, B. (2008). Recognition of facial expressions is influenced by emotional scene gist. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 8(3), 264-272. https://doi.org/10.3758/CABN.8.3.264
Righart, R., & De Gelder, B. (2008). Recognition of facial expressions is influenced by emotional scene gist. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 8(3), 264-272. https://doi.org/10.3758/CABN.8.3.264
Chapters
 Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Social perception: Understanding other people's intentions and emotions through their actions. In T. Striano & V. Reid (Eds.), Social cognition: Development, neuroscience and autism (pp. 67-78). Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2008). Social perception: Understanding other people's intentions and emotions through their actions. In T. Striano & V. Reid (Eds.), Social cognition: Development, neuroscience and autism (pp. 67-78). Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
 Verstraten, F.A.J. & de Gelder, B. (2008). Het brein en visueel waarnemen. In F. Wijnen & F.A.J. Verstraten (Eds), Brein te kijk: Een verkenning van de cognitieve neurowetenschappen. London: Harcourt.
Verstraten, F.A.J. & de Gelder, B. (2008). Het brein en visueel waarnemen. In F. Wijnen & F.A.J. Verstraten (Eds), Brein te kijk: Een verkenning van de cognitieve neurowetenschappen. London: Harcourt.
2007
 Wijnen, V.J.M., van Boxtel, G.J.M., Eilander, H.J., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Mismatch negativity predicts recovery from the vegetative state. Clinical Neurophysiology, 118, 597-605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2006.11.020
Wijnen, V.J.M., van Boxtel, G.J.M., Eilander, H.J., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Mismatch negativity predicts recovery from the vegetative state. Clinical Neurophysiology, 118, 597-605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2006.11.020
 Righart, R. & de Gelder, B. (2007). Impaired face and body perception in developmental prosopagnosia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 104(42), 17234–17238. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0707753104
Righart, R. & de Gelder, B. (2007). Impaired face and body perception in developmental prosopagnosia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 104(42), 17234–17238. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0707753104
 Grèzes, J., Pichon, S., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Perceiving fear in dynamic body expressions.NeuroImage, 35(2), 959-967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.11.030
Grèzes, J., Pichon, S., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Perceiving fear in dynamic body expressions.NeuroImage, 35(2), 959-967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.11.030
 de Gelder, B. & Tamietto, M. (2007). Affective blindsight. Scholarpedia, 2(10), 3555.
de Gelder, B. & Tamietto, M. (2007). Affective blindsight. Scholarpedia, 2(10), 3555.
 Magnée, M. J. C. M., de Gelder, B., van Engeland, H., & Kemner, C. (2007). Facial electromyographic responses to emotional information from faces and voices in individuals with Pervasive Developmental Disorder. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48(11), 1122-1130. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01779.x
Magnée, M. J. C. M., de Gelder, B., van Engeland, H., & Kemner, C. (2007). Facial electromyographic responses to emotional information from faces and voices in individuals with Pervasive Developmental Disorder. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48(11), 1122-1130. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01779.x
 van Heijnsbergen, C.C.R.J., Meeren, H.K.M., Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Rapid detection of fear in body expressions, an ERP study. Brain Research, 1186, 233-241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2007.09.093
van Heijnsbergen, C.C.R.J., Meeren, H.K.M., Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Rapid detection of fear in body expressions, an ERP study. Brain Research, 1186, 233-241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2007.09.093
 Van den Stock, J., Righart, R., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Body expressions influence recognition of emotions in the face and voice. Emotion, 7(3), 487-494. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/1528-3542.7.3.487
Van den Stock, J., Righart, R., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Body expressions influence recognition of emotions in the face and voice. Emotion, 7(3), 487-494. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/1528-3542.7.3.487
 Magnée, M. J. C. M., Stekelenburg, J. J., Kemner, C., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Similar facial EMG responses to faces, voices, and body expressions. NeuroReport, 18(4), 369-372. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32801776e6
Magnée, M. J. C. M., Stekelenburg, J. J., Kemner, C., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Similar facial EMG responses to faces, voices, and body expressions. NeuroReport, 18(4), 369-372. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32801776e6
 Tamietto, M., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Fast recognition of social emotions takes the whole brain: interhemispheric cooperation in the absence of cerebral asymmetry. Neuropsychologia, 45, 836-843. Fast recognition of social emotions takes the whole brain: Interhemispheric
cooperation in the absence of cerebral asymmetry
Tamietto, M., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Fast recognition of social emotions takes the whole brain: interhemispheric cooperation in the absence of cerebral asymmetry. Neuropsychologia, 45, 836-843. Fast recognition of social emotions takes the whole brain: Interhemispheric
cooperation in the absence of cerebral asymmetry
 Tamietto, M., Geminiani, G., Genero, R., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Seeing fearful body language overcomes attentional deficits in patients with neglect. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19, 445-454. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2007.19.3.445
Tamietto, M., Geminiani, G., Genero, R., & de Gelder, B. (2007). Seeing fearful body language overcomes attentional deficits in patients with neglect. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19, 445-454. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2007.19.3.445
 Vroomen, J., Van Linden, S., de Gelder, B. & Bertelson, P. (2007). Visual recalibration and selective adaptation in auditory–visual speech perception: Contrasting build-up courses.Neuropsychologia, 45(3), 572-577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.01.031
Vroomen, J., Van Linden, S., de Gelder, B. & Bertelson, P. (2007). Visual recalibration and selective adaptation in auditory–visual speech perception: Contrasting build-up courses.Neuropsychologia, 45(3), 572-577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.01.031
2006
 Tamietto, M., Corazzini, L. L., de Gelder, B. & Geminiani, G. (2006). Functional asymmetry and interhemispheric cooperation in the perception of emotions from facial expressions. Experimental Brain Research, 171(3), 389-404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0279-4
Tamietto, M., Corazzini, L. L., de Gelder, B. & Geminiani, G. (2006). Functional asymmetry and interhemispheric cooperation in the perception of emotions from facial expressions. Experimental Brain Research, 171(3), 389-404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0279-4
 Le Grand, R., Cooper, P. A., Mondloch, C. J., Lewis, T. L., Sagiv, N., de Gelder, B. & Maurer, D. (2006). What aspects of face processing are impaired in developmental prosopagnosia? Brain and Cognition, 61, 139-158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2005.11.005
Le Grand, R., Cooper, P. A., Mondloch, C. J., Lewis, T. L., Sagiv, N., de Gelder, B. & Maurer, D. (2006). What aspects of face processing are impaired in developmental prosopagnosia? Brain and Cognition, 61, 139-158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2005.11.005
 de Gelder, B. & Hadjikhani, N. (2006). Non-conscious recognition of emotional body language.Neuroreport, 17(6), 583-586.
de Gelder, B. & Hadjikhani, N. (2006). Non-conscious recognition of emotional body language.Neuroreport, 17(6), 583-586.
 de Gelder, B. (2006). Toward a biological theory of emotional body language. Biological Theory, 1(2), 130-132.
de Gelder, B. (2006). Toward a biological theory of emotional body language. Biological Theory, 1(2), 130-132.
 de Gelder, B. (2006). Towards the neurobiology of emotional body language. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7(3), 242-249. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1872
de Gelder, B. (2006). Towards the neurobiology of emotional body language. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7(3), 242-249. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1872
 de Gelder, B., Meeren, H. K. M., Righart, R., Van den Stock, J. , van de Riet, W. A. C., & Tamietto, M. (2006) . Beyond the face: Exploring rapid influences of context on face processing. Progress in Brain Research, 155, 37-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(06)55003-4
de Gelder, B., Meeren, H. K. M., Righart, R., Van den Stock, J. , van de Riet, W. A. C., & Tamietto, M. (2006) . Beyond the face: Exploring rapid influences of context on face processing. Progress in Brain Research, 155, 37-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(06)55003-4
 Righart, R., & de Gelder, B. (2006). Context influences early perceptual analysis of faces. An electrophysiological study. Cerebral Cortex, 16, 1249-1257. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhj066
Righart, R., & de Gelder, B. (2006). Context influences early perceptual analysis of faces. An electrophysiological study. Cerebral Cortex, 16, 1249-1257. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhj066
 Wijnen, V. J. M., Heutink, M., van Boxtel, G. J. M., Eilander, H. J. & de Gelder, B. (2006). Autonomic reactivity to sensory stimulation is related to recovery from severe traumatic brain injury in adolescents. Clinical Neurophysiology, 17, 1794-1807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2006.03.006
Wijnen, V. J. M., Heutink, M., van Boxtel, G. J. M., Eilander, H. J. & de Gelder, B. (2006). Autonomic reactivity to sensory stimulation is related to recovery from severe traumatic brain injury in adolescents. Clinical Neurophysiology, 17, 1794-1807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2006.03.006
2005
 de Gelder, B., Morris, J.S., & Dolan, R.J. (2005). Unconscious fear influences emotional awareness of faces and voices. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA,102, 18682-18687. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0509179102
de Gelder, B., Morris, J.S., & Dolan, R.J. (2005). Unconscious fear influences emotional awareness of faces and voices. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA,102, 18682-18687. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0509179102
 Meeren, H. K. M., van Heijnsbergen, C., & de Gelder, B. (2005). Rapid perceptual integration of facial expression and emotional body language. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 102, 16518-16523. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507650102
Meeren, H. K. M., van Heijnsbergen, C., & de Gelder, B. (2005). Rapid perceptual integration of facial expression and emotional body language. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 102, 16518-16523. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507650102
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., de Jong, J. J., Masthoff, E. D., Trompenaars, F. J., & Hodiamont, P. (2005). Multisensory integration of emotional faces and voices in schizophrenics. Schizophrenia Research, 72, 195-203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2004.02.013
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., de Jong, J. J., Masthoff, E. D., Trompenaars, F. J., & Hodiamont, P. (2005). Multisensory integration of emotional faces and voices in schizophrenics. Schizophrenia Research, 72, 195-203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2004.02.013
 Pourtois, G., de Gelder, B., Bol, A., & Crommelinck, M. (2005). Perception of facial expressions and voices and of their combination in the human brain. Cortex, 41(1), 49-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-9452(08)70177-1
Pourtois, G., de Gelder, B., Bol, A., & Crommelinck, M. (2005). Perception of facial expressions and voices and of their combination in the human brain. Cortex, 41(1), 49-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-9452(08)70177-1
 de Gelder, B., & Stekelenburg, J. J. (2005). Naso-temporal asymmetry of the N170 for processing faces in normal viewers but not in developmental prosopagnosia. Neuroscience Letters, 376, 40-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.11.047
de Gelder, B., & Stekelenburg, J. J. (2005). Naso-temporal asymmetry of the N170 for processing faces in normal viewers but not in developmental prosopagnosia. Neuroscience Letters, 376, 40-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.11.047
 Frissen, I., Vroomen, J., de Gelder, B., & Bertelson, P. (2005). The aftereffects of ventriloquism: Generalization across sound-frequencies. Acta Psychologica, 118 (1), 93-100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2004.10.004
Frissen, I., Vroomen, J., de Gelder, B., & Bertelson, P. (2005). The aftereffects of ventriloquism: Generalization across sound-frequencies. Acta Psychologica, 118 (1), 93-100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2004.10.004
Chapters
 Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2005). Contagion motrice et contagion émotionnelle. In C. Andrès, C. Barthélémy, A. Berthoz, J. Massion & B. Rogé (Eds.), Autisme, cerveau et développement : de la recherche à la pratique (pp. 293-318). Paris: Odile Jacob.
Grèzes, J., & de Gelder, B. (2005). Contagion motrice et contagion émotionnelle. In C. Andrès, C. Barthélémy, A. Berthoz, J. Massion & B. Rogé (Eds.), Autisme, cerveau et développement : de la recherche à la pratique (pp. 293-318). Paris: Odile Jacob.
 de Gelder, B. (2005). Nonconscious emotions: New findings and perspectives on nonconscious facial expression recognition and its voice and whole body contexts. In L. Feldman Barrett, P. M. Niedenthal & P. Winkielman (Eds.), Emotion and consciousness (pp. 123-149). New York-London: The Guilford Press.
de Gelder, B. (2005). Nonconscious emotions: New findings and perspectives on nonconscious facial expression recognition and its voice and whole body contexts. In L. Feldman Barrett, P. M. Niedenthal & P. Winkielman (Eds.), Emotion and consciousness (pp. 123-149). New York-London: The Guilford Press.
2004
 Vroomen, J., Keetels, M., de Gelder, B. & Bertelson, P. (2004). Recalibration of temporal order perception by exposure to audio-visual asynchrony. Cognitive Brain Research, 22(1), 32-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2004.07.003
Vroomen, J., Keetels, M., de Gelder, B. & Bertelson, P. (2004). Recalibration of temporal order perception by exposure to audio-visual asynchrony. Cognitive Brain Research, 22(1), 32-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2004.07.003
 de Gelder, B., Snyder, J., Greve, D., Gerard, G. & Hadjikhani, N. (2004). Fear fosters flight: A mechanism for fear contagion when perceiving emotion expressed by a whole body. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101(47), 16701-16706. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407042101
de Gelder, B., Snyder, J., Greve, D., Gerard, G. & Hadjikhani, N. (2004). Fear fosters flight: A mechanism for fear contagion when perceiving emotion expressed by a whole body. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101(47), 16701-16706. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407042101
 Vroomen, J. & de Gelder, B. (2004). Temporal vetriloquism: Sound modulates the flash-lag effect.Journal of Experimental Psychology. Human Perception and Performance, 30(3), 513-518. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0096-1523.30.3.513
Vroomen, J. & de Gelder, B. (2004). Temporal vetriloquism: Sound modulates the flash-lag effect.Journal of Experimental Psychology. Human Perception and Performance, 30(3), 513-518. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0096-1523.30.3.513
 Kilgour, A. R., de Gelder, B., & Lederman, S. J. (2004). Haptic face recognition and prosopagnosia.Neuropsychologia, 42(6), 707-712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2003.11.021
Kilgour, A. R., de Gelder, B., & Lederman, S. J. (2004). Haptic face recognition and prosopagnosia.Neuropsychologia, 42(6), 707-712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2003.11.021
 Stekelenburg, J. J., & de Gelder, B. (2004). The neural correlates of perceiving human bodies: an ERP study on the body-inversion effect. Neuroreport, 15(5), 777-780. DOI: 10.1097/01.wnr.0000119730.93564.e8
Stekelenburg, J. J., & de Gelder, B. (2004). The neural correlates of perceiving human bodies: an ERP study on the body-inversion effect. Neuroreport, 15(5), 777-780. DOI: 10.1097/01.wnr.0000119730.93564.e8
 Stekelenburg, J. J., Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2004). Illusory sound shifts induced by the ventriloquist illusion evoke the mismatch negativity. Neuroscience Letters, 357(3), 163-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2003.12.085
Stekelenburg, J. J., Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2004). Illusory sound shifts induced by the ventriloquist illusion evoke the mismatch negativity. Neuroscience Letters, 357(3), 163-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2003.12.085
 Vroomen, J., van Linden, B., Keetels, M., De Gelder, B., & Bertelson, P. (2004). Selective adaptation and recalibration of auditory speech by lipread information: Dissipation. Speech Communication, 44, 55-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.specom.2004.03.009
Vroomen, J., van Linden, B., Keetels, M., De Gelder, B., & Bertelson, P. (2004). Selective adaptation and recalibration of auditory speech by lipread information: Dissipation. Speech Communication, 44, 55-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.specom.2004.03.009
Chapters
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J. & Pourtois, G. (2004). Multisensory perception of affect, its time course and its neural basis. In G. Calvert, C. Spence & B.E. Stein (Eds.), Handbook of multisensory processes (pp. 581-596). Cambridge, MA: MIT.
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J. & Pourtois, G. (2004). Multisensory perception of affect, its time course and its neural basis. In G. Calvert, C. Spence & B.E. Stein (Eds.), Handbook of multisensory processes (pp. 581-596). Cambridge, MA: MIT.
 Bertelson, P., & de Gelder, B. (2004). The psychology of multimodal perception. In C. Spence & J. Driver (Eds.), Crossmodal space and crossmodal attention (pp. 151-177). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Bertelson, P., & de Gelder, B. (2004). The psychology of multimodal perception. In C. Spence & J. Driver (Eds.), Crossmodal space and crossmodal attention (pp. 151-177). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
 Vroomen, J. & de Gelder, B. (2004). Perceptual effects of cross-modal stimulation: Ventriloquism and the freezing phenomenon. In G. Calvert, C. Spence & B.E. Stein (Eds.), Handbook of multisensory processes (pp. 141-150). Cambridge, MA: MIT.
Vroomen, J. & de Gelder, B. (2004). Perceptual effects of cross-modal stimulation: Ventriloquism and the freezing phenomenon. In G. Calvert, C. Spence & B.E. Stein (Eds.), Handbook of multisensory processes (pp. 141-150). Cambridge, MA: MIT.
2003
 Bertelson, P., Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2003). Visual recalibration of auditory speech identification: A McGurk aftereffect. Psychological Science, 14 (6), 592-597. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0956-7976.2003.psci_1470.x
Bertelson, P., Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2003). Visual recalibration of auditory speech identification: A McGurk aftereffect. Psychological Science, 14 (6), 592-597. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0956-7976.2003.psci_1470.x
 de Gelder, B., & Bertelson, P. (2003). Multisensory integration, perception and ecological validity.Trends in Cognitive Science, 7 (10), 460-467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2003.08.014
de Gelder, B., & Bertelson, P. (2003). Multisensory integration, perception and ecological validity.Trends in Cognitive Science, 7 (10), 460-467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2003.08.014
 de Gelder, B., Frissen, I., Barton, J., & Hadjikhani, N. (2003). A modulatory role for facial expressions in prosopagnosia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the U S A, 100(22), 13105-13110. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1735530100
de Gelder, B., Frissen, I., Barton, J., & Hadjikhani, N. (2003). A modulatory role for facial expressions in prosopagnosia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the U S A, 100(22), 13105-13110. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1735530100
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Annen, L., Masthof, E., & Hodiamont, P. (2003). Audio-visual integration in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 59 (2-3), 211-218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-9964(01)00344-9
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Annen, L., Masthof, E., & Hodiamont, P. (2003). Audio-visual integration in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 59 (2-3), 211-218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-9964(01)00344-9
 Frissen, I., Vroomen, J., de Gelder, B., & Bertelson, P. (2003). The aftereffects of ventriloquism: are they sound-frequency specific? Acta Psychologica (Amst), 113 (3), 315-327. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-6918(03)00043-X
Frissen, I., Vroomen, J., de Gelder, B., & Bertelson, P. (2003). The aftereffects of ventriloquism: are they sound-frequency specific? Acta Psychologica (Amst), 113 (3), 315-327. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-6918(03)00043-X
 Hadjikhani, N., & de Gelder, B. (2003). Seeing fearful body expressions activates the fusiform cortex and amygdala. Current Biology, 13 (24), 2201-2205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2003.11.049
Hadjikhani, N., & de Gelder, B. (2003). Seeing fearful body expressions activates the fusiform cortex and amygdala. Current Biology, 13 (24), 2201-2205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2003.11.049
 Teunisse, J.P., & de Gelder, B. (2003). Face processing in adolescents with autistic disorder: the inversion and composite effects. Brain and Cognition, 52 (3), 285-294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-2626(03)00042-3
Teunisse, J.P., & de Gelder, B. (2003). Face processing in adolescents with autistic disorder: the inversion and composite effects. Brain and Cognition, 52 (3), 285-294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-2626(03)00042-3
 Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2003). Visual motion influences the contingent auditory motion aftereffect. Psychological Science, 14 (4), 357-361. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9280.24431
Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2003). Visual motion influences the contingent auditory motion aftereffect. Psychological Science, 14 (4), 357-361. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9280.24431
2002
 de Gelder, B., Pourtois, G., & Weiskrantz, L. (2002). Fear recognition in the voice is modulated by unconsciously recognized facial expressions but not by unconsciously recognized affective pictures. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U S A, 99 (6), 4121-4126. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.062018499
de Gelder, B., Pourtois, G., & Weiskrantz, L. (2002). Fear recognition in the voice is modulated by unconsciously recognized facial expressions but not by unconsciously recognized affective pictures. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U S A, 99 (6), 4121-4126. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.062018499
 Hadjikhani, N., & de Gelder, B. (2002). Neural basis of prosopagnosia: An fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 16 (3), 176-182. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.10043
Hadjikhani, N., & de Gelder, B. (2002). Neural basis of prosopagnosia: An fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 16 (3), 176-182. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.10043
 Pourtois, G., & de Gelder, B. (2002). Semantic factors influence multisensory pairing: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Neuroreport, 13 (12), 1567-1573.
Pourtois, G., & de Gelder, B. (2002). Semantic factors influence multisensory pairing: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Neuroreport, 13 (12), 1567-1573.
 de Jong, J., de Gelder, B. & Hodiamont, P.P.G. (2002). Emotieherkenning en cross-modaliteit bij schizofreniepatiënten. Tijdschrift voor Psychiatrie, 44 (11), 747-752.
de Jong, J., de Gelder, B. & Hodiamont, P.P.G. (2002). Emotieherkenning en cross-modaliteit bij schizofreniepatiënten. Tijdschrift voor Psychiatrie, 44 (11), 747-752.
 Pourtois, G., Debatisse, D., Despland, P. A., & de Gelder, B. (2002). Facial expressions modulate the time course of long latency auditory brain potentials. Brain Research. Cognitive Brain Research, 14 (1), 99-105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-6410(02)00064-2
Pourtois, G., Debatisse, D., Despland, P. A., & de Gelder, B. (2002). Facial expressions modulate the time course of long latency auditory brain potentials. Brain Research. Cognitive Brain Research, 14 (1), 99-105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-6410(02)00064-2
 Rouw, R., & de Gelder, B. (2002). Impaired face recognition does not preclude intact whole face perception. Visual Cognition, 9 (6), 689-718. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506280143000223
Rouw, R., & de Gelder, B. (2002). Impaired face recognition does not preclude intact whole face perception. Visual Cognition, 9 (6), 689-718. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506280143000223
2001
 Bertelson, P., Vroomen, J., Aschersleben, G., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Object identity decisions: At what processing levels? Or: Why the cantaloupe might work: Commentary. Cahiers de Psychologie Cognitive/Current Psychology of Cognition, 20 (3-4), 177-182.
Bertelson, P., Vroomen, J., Aschersleben, G., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Object identity decisions: At what processing levels? Or: Why the cantaloupe might work: Commentary. Cahiers de Psychologie Cognitive/Current Psychology of Cognition, 20 (3-4), 177-182.
 de Gelder, B., Pourtois, G., van Raamsdonk, M., Vroomen, J., & Weiskrantz, L. (2001). Unseen stimuli modulate conscious visual experience: Evidence from inter-hemispheric summation.Neuroreport, 12 (2), 385-391.
de Gelder, B., Pourtois, G., van Raamsdonk, M., Vroomen, J., & Weiskrantz, L. (2001). Unseen stimuli modulate conscious visual experience: Evidence from inter-hemispheric summation.Neuroreport, 12 (2), 385-391.
 de Gelder, B., & Rouw, R. (2001). Beyond localisation: a dynamical dual route account of face recognition. Acta Psychologica (Amst), 107 (1-3), 183-207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-6918(01)00024-5
de Gelder, B., & Rouw, R. (2001). Beyond localisation: a dynamical dual route account of face recognition. Acta Psychologica (Amst), 107 (1-3), 183-207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-6918(01)00024-5
 Dolan, R.J., Morris, J.S., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Crossmodal binding of fear in voice and face.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U S A, 98 (17), 10006-10010. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.171288598
Dolan, R.J., Morris, J.S., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Crossmodal binding of fear in voice and face.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U S A, 98 (17), 10006-10010. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.171288598
 Morris, J.S., de Gelder, B., Weiskrantz, L., & Dolan, R. J. (2001). Differential extrageniculostriate and amygdala responses to presentation of emotional faces in a cortically blind field. Brain, 124, 1241-1252. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/124.6.1241
Morris, J.S., de Gelder, B., Weiskrantz, L., & Dolan, R. J. (2001). Differential extrageniculostriate and amygdala responses to presentation of emotional faces in a cortically blind field. Brain, 124, 1241-1252. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/124.6.1241
 Pourtois, G., Vandermeeren, Y., Olivier, E., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Event-related TMS over the right posterior parietal cortex induces ipsilateral visuo-spatial interference. Neuroreport, 12 (11), 2369-2374.
Pourtois, G., Vandermeeren, Y., Olivier, E., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Event-related TMS over the right posterior parietal cortex induces ipsilateral visuo-spatial interference. Neuroreport, 12 (11), 2369-2374.
 Teunisse, J-P., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Impaired categorical perception of facial expressions in high-functioning adolescents with autism. Child Neuropsychology, 7 (1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1076/chin.7.1.1.3150
Teunisse, J-P., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Impaired categorical perception of facial expressions in high-functioning adolescents with autism. Child Neuropsychology, 7 (1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1076/chin.7.1.1.3150
 Vroomen, J., Bertelson, P., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Directing spatial attention towards the illusory location of a ventriloquized sound. Acta Psychologica (Amst), 108 (1), 21-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-6918(00)00068-8
Vroomen, J., Bertelson, P., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Directing spatial attention towards the illusory location of a ventriloquized sound. Acta Psychologica (Amst), 108 (1), 21-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-6918(00)00068-8
 Vroomen, J., Bertelson, P., & de Gelder, B. (2001). The ventriloquist effect does not depend on the direction of automatic visual attention. Perception & Psychophysics, 63 (4), 651-659. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03194427
Vroomen, J., Bertelson, P., & de Gelder, B. (2001). The ventriloquist effect does not depend on the direction of automatic visual attention. Perception & Psychophysics, 63 (4), 651-659. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03194427
 Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Lipreading and the compensation for coarticulation mechanism. Language and Cognitive Processes, 16 (5-6), 661-672. https://doi.org/10.1080/01690960143000092
Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Lipreading and the compensation for coarticulation mechanism. Language and Cognitive Processes, 16 (5-6), 661-672. https://doi.org/10.1080/01690960143000092
 Vroomen, J., Driver, J., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Is cross-modal integration of emotional expressions independent of attentional resources? Cognitive, Affective and Behavioral Neuroscience, 1 (4), 382-387. https://doi.org/10.3758/CABN.1.4.382
Vroomen, J., Driver, J., & de Gelder, B. (2001). Is cross-modal integration of emotional expressions independent of attentional resources? Cognitive, Affective and Behavioral Neuroscience, 1 (4), 382-387. https://doi.org/10.3758/CABN.1.4.382
Edited books
 De Gelder, B., de Haan, E.H.F., & Heywood, C.A. (2001). Out of mind: Varieties of unconscious processes. London: Oxford University Press.
De Gelder, B., de Haan, E.H.F., & Heywood, C.A. (2001). Out of mind: Varieties of unconscious processes. London: Oxford University Press.
2000
 Bertelson, P., Pavani, F., Ladavas, E., Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2000). Ventriloquism in patients with unilateral visual neglect. Neuropsychologia, 38 (12), 1634-1642. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(00)00067-1
Bertelson, P., Pavani, F., Ladavas, E., Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2000). Ventriloquism in patients with unilateral visual neglect. Neuropsychologia, 38 (12), 1634-1642. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(00)00067-1
 Bertelson, P., Vroomen, J., de Gelder, B., & Driver, J. (2000). The ventriloquist effect does not depend on the direction of deliberate visual attention. Perception & Psychophysics, 62 (2), 321-332. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03205552
Bertelson, P., Vroomen, J., de Gelder, B., & Driver, J. (2000). The ventriloquist effect does not depend on the direction of deliberate visual attention. Perception & Psychophysics, 62 (2), 321-332. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03205552
 Bosman, A. M., van Leerdam, M., & de Gelder, B. (2000). The /O/ in OVER is different from the /O/ in OTTER: Phonological effects in children with and without dyslexia. Developmental Psychology, 36(6), 817-825. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0012-1649.36.6.817
Bosman, A. M., van Leerdam, M., & de Gelder, B. (2000). The /O/ in OVER is different from the /O/ in OTTER: Phonological effects in children with and without dyslexia. Developmental Psychology, 36(6), 817-825. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0012-1649.36.6.817
 de Gelder, B. (2000). More to seeing than meets the eye. Science, 289 (5482), 1148-1149. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.289.5482.1148
de Gelder, B. (2000). More to seeing than meets the eye. Science, 289 (5482), 1148-1149. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.289.5482.1148
 de Gelder, B., Pourtois, G., Vroomen, J., & Bachoud-Levi, A.C. (2000). Covert processing of faces in prosopagnosia is restricted to facial expressions: Evidence from cross-modal bias. Brain Cognition, 44 (3), 425-444. https://doi.org/10.1006/brcg.1999.1203
de Gelder, B., Pourtois, G., Vroomen, J., & Bachoud-Levi, A.C. (2000). Covert processing of faces in prosopagnosia is restricted to facial expressions: Evidence from cross-modal bias. Brain Cognition, 44 (3), 425-444. https://doi.org/10.1006/brcg.1999.1203
 de Gelder, B., & Rouw, R. (2000a). Configural face processes in acquired and developmental prosopagnosia: evidence for two separate face systems? Neuroreport, 11 (14), 3145-3150.
de Gelder, B., & Rouw, R. (2000a). Configural face processes in acquired and developmental prosopagnosia: evidence for two separate face systems? Neuroreport, 11 (14), 3145-3150.
 de Gelder, B., & Rouw, R. (2000b). Paradoxical configuration effects for faces and objects in prosopagnosia. Neuropsychologia, 38 (9), 1271-1279. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(00)00039-7
de Gelder, B., & Rouw, R. (2000b). Paradoxical configuration effects for faces and objects in prosopagnosia. Neuropsychologia, 38 (9), 1271-1279. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(00)00039-7
 de Gelder, B., & Rouw, R. (2000). Structural encoding precludes recognition of face parts in prosopagnosia. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 17 (1-3), 89-102. https://doi.org/10.1080/026432900380508
de Gelder, B., & Rouw, R. (2000). Structural encoding precludes recognition of face parts in prosopagnosia. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 17 (1-3), 89-102. https://doi.org/10.1080/026432900380508
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (2000). Bimodal emotion perception: Integration across separate modalities, cross-modal perceptual grouping or perception of multimodal events? Cognition and Emotion, 14 (3), 321-324. https://doi.org/10.1080/026999300378842
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (2000). Bimodal emotion perception: Integration across separate modalities, cross-modal perceptual grouping or perception of multimodal events? Cognition and Emotion, 14 (3), 321-324. https://doi.org/10.1080/026999300378842
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (2000). The perception of emotions by ear and by eye. Cognition & Emotion, 14 (3), 289-311. https://doi.org/10.1080/026999300378824
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (2000). The perception of emotions by ear and by eye. Cognition & Emotion, 14 (3), 289-311. https://doi.org/10.1080/026999300378824
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Pourtois, G., & Weiskrantz, L. (2000). Affective blindsight: Are we blindly led by emotions? Response to Heywood and Kentridge (2000). Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4(4), 126-127. DOI: 10.1016/s1364-6613(00)01470-4
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Pourtois, G., & Weiskrantz, L. (2000). Affective blindsight: Are we blindly led by emotions? Response to Heywood and Kentridge (2000). Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4(4), 126-127. DOI: 10.1016/s1364-6613(00)01470-4
 Peterson, M.A., de Gelder, B., Rapcsak, S.Z., Gerhardstein, P.C., & Bachoud-Levi, A. (2000). Object memory effects on figure assignment: Conscious object recognition is not necessary or sufficient.Vision Research, 40 (10-12), 1549-1567. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0042-6989(00)00053-5
Peterson, M.A., de Gelder, B., Rapcsak, S.Z., Gerhardstein, P.C., & Bachoud-Levi, A. (2000). Object memory effects on figure assignment: Conscious object recognition is not necessary or sufficient.Vision Research, 40 (10-12), 1549-1567. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0042-6989(00)00053-5
 Pourtois, G., de Gelder, B., Rossion, B., & Weiskrantz, L. (2000). Time-course of early visual extrastriate activity in a blindsight patient using event related potentials. Abstract. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, (supplement), 72.
Pourtois, G., de Gelder, B., Rossion, B., & Weiskrantz, L. (2000). Time-course of early visual extrastriate activity in a blindsight patient using event related potentials. Abstract. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, (supplement), 72.
 Pourtois, G., de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Rossion, B., & Crommelinck, M. (2000). The time-course of intermodal binding between seeing and hearing affective information. Neuroreport, 11 (6), 1329-1333.
Pourtois, G., de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Rossion, B., & Crommelinck, M. (2000). The time-course of intermodal binding between seeing and hearing affective information. Neuroreport, 11 (6), 1329-1333.
 Rossion, B., de Gelder, B., Pourtois, G., Guerit, J. M., & Weiskrantz, L. (2000). Early extrastriate activity without primary visual cortex in humans. Neuroscience Letters, 279 (1), 25-28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(99)00926-X
Rossion, B., de Gelder, B., Pourtois, G., Guerit, J. M., & Weiskrantz, L. (2000). Early extrastriate activity without primary visual cortex in humans. Neuroscience Letters, 279 (1), 25-28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(99)00926-X
 Rossion, B., Dricot, L., Devolder, A., Bodart, J. M., Crommelinck, M., De Gelder, B., & Zoontjes, R. (2000). Hemispheric asymmetries for whole-based and part-based face processing in the human fusiform gyrus. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12 (5), 793-802. DOI: 10.1162/089892900562606
Rossion, B., Dricot, L., Devolder, A., Bodart, J. M., Crommelinck, M., De Gelder, B., & Zoontjes, R. (2000). Hemispheric asymmetries for whole-based and part-based face processing in the human fusiform gyrus. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12 (5), 793-802. DOI: 10.1162/089892900562606
 Toumainen, J., de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (2000). Different temporal dynamics in the utilization of word stress and vowel harmony in lexical segmentation: An event-related potential study.International Journal of Psychology, 35 (3-4), 39-39.
Toumainen, J., de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (2000). Different temporal dynamics in the utilization of word stress and vowel harmony in lexical segmentation: An event-related potential study.International Journal of Psychology, 35 (3-4), 39-39.
 Vroomen, J., & Gelder, B. (2000). Crossmodal integration: A good fit is no criterion. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4 (2), 37-38.
Vroomen, J., & Gelder, B. (2000). Crossmodal integration: A good fit is no criterion. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4 (2), 37-38.
 Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2000). Sound enhances visual perception: Cross-modal effects of auditory organization on vision. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 26 (5), 1583-1590. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0096-1523.26.5.1583
Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2000). Sound enhances visual perception: Cross-modal effects of auditory organization on vision. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 26 (5), 1583-1590. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0096-1523.26.5.1583
 Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2000a). Why not model spoken word recognition instead of phoneme monitoring? Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 23 (3), 349-350. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X00493246
Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (2000a). Why not model spoken word recognition instead of phoneme monitoring? Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 23 (3), 349-350. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X00493246
Chapters
 de Gelder, B. (2000). Recognizing emotions by ear and by eye. In R. D. Lane & L. Nadel (Eds.), Cognitive neuroscience of emotion. Series in affective science (pp. 84-105). London: Oxford University Press.
de Gelder, B. (2000). Recognizing emotions by ear and by eye. In R. D. Lane & L. Nadel (Eds.), Cognitive neuroscience of emotion. Series in affective science (pp. 84-105). London: Oxford University Press.
1999
 Bertelson, P., Chen, H.-C., Tseng, C.-H., Ko, H.-W. & de Gelder, B. (1999). Phonological awareness and orthographic experience in Chinese readers. Journal of Chinese Linguistics, 13,26-39. https://www.jstor.org/stable/23826108
Bertelson, P., Chen, H.-C., Tseng, C.-H., Ko, H.-W. & de Gelder, B. (1999). Phonological awareness and orthographic experience in Chinese readers. Journal of Chinese Linguistics, 13,26-39. https://www.jstor.org/stable/23826108
 Böcker, K. B., Bastiaansen, M. C., Vroomen, J., Brunia, C. H., & de Gelder, B. (1999). An ERP correlate of metrical stress in spoken word recognition. Psychophysiology, 36 (6), 706-720. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-8986.3660706
Böcker, K. B., Bastiaansen, M. C., Vroomen, J., Brunia, C. H., & de Gelder, B. (1999). An ERP correlate of metrical stress in spoken word recognition. Psychophysiology, 36 (6), 706-720. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-8986.3660706
 de Gelder, B., Böcker, K. B., Tuomainen, J., Hensen, M., & Vroomen, J. (1999). The combined perception of emotion from voice and face: early interaction revealed by human electric brain responses. Neuroscience Letters, 260 (2), 133-136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(98)00963-X
de Gelder, B., Böcker, K. B., Tuomainen, J., Hensen, M., & Vroomen, J. (1999). The combined perception of emotion from voice and face: early interaction revealed by human electric brain responses. Neuroscience Letters, 260 (2), 133-136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(98)00963-X
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Pourtois, G., & Weiskrantz, L. (1999). Non-conscious recognition of affect in the absence of striate cortex. Neuroreport, 10 (18), 3759-3763.
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Pourtois, G., & Weiskrantz, L. (1999). Non-conscious recognition of affect in the absence of striate cortex. Neuroreport, 10 (18), 3759-3763.
 Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (1999). Lexical access of resyllabified words: evidence from phoneme monitoring. Mem Cognit, 27 (3), 413-421. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03211537
Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (1999). Lexical access of resyllabified words: evidence from phoneme monitoring. Mem Cognit, 27 (3), 413-421. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03211537
Chapters
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & Pourtois, G. (1999). Seeing cries and hearing smiles: Crossmodal perception of emotional expressions. In G. Aschersleben & T. Bachmann (Eds.), Cognitive contributions to the perception of spatial and temporal events. Advances in psychology, 129 (pp. 425-438). Amsterdam, Netherlands: North-Holland/Elsevier Science Publishers. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4115(99)80040-5
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & Pourtois, G. (1999). Seeing cries and hearing smiles: Crossmodal perception of emotional expressions. In G. Aschersleben & T. Bachmann (Eds.), Cognitive contributions to the perception of spatial and temporal events. Advances in psychology, 129 (pp. 425-438). Amsterdam, Netherlands: North-Holland/Elsevier Science Publishers. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4115(99)80040-5
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J.H.M. & Bertelson, P. (1999). The role of face parts: The perception of emotions in the voice and face. In L. Grim Cabral & J. Morais (Eds.), Investigando a linguagem(pp. 262-266). Florianópolis: Mulheres.
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J.H.M. & Bertelson, P. (1999). The role of face parts: The perception of emotions in the voice and face. In L. Grim Cabral & J. Morais (Eds.), Investigando a linguagem(pp. 262-266). Florianópolis: Mulheres.
1998
 Bartolomeo, P., Bachoud-Levi, A. C., de Gelder, B., Denes, G., Dalla Barba, G., Brugieres, P., & Degos, J. D. (1998). Multiple-domain dissociation between impaired visual perception and preserved mental imagery in a patient with bilateral extrastriate lesions. Neuropsychologia, 36 (3), 239-249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(97)00103-6
Bartolomeo, P., Bachoud-Levi, A. C., de Gelder, B., Denes, G., Dalla Barba, G., Brugieres, P., & Degos, J. D. (1998). Multiple-domain dissociation between impaired visual perception and preserved mental imagery in a patient with bilateral extrastriate lesions. Neuropsychologia, 36 (3), 239-249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3932(97)00103-6
 de Gelder, B., Bachoud-Levi, A. C., & Degos, J. D. (1998). Inversion superiority in visual agnosia may be common to a variety of orientation polarised objects besides faces. Vision Research, 38(18), 2855-2861. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0042-6989(97)00458-6
de Gelder, B., Bachoud-Levi, A. C., & Degos, J. D. (1998). Inversion superiority in visual agnosia may be common to a variety of orientation polarised objects besides faces. Vision Research, 38(18), 2855-2861. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0042-6989(97)00458-6
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1998). Impaired speech perception in poor readers: Evidence from hearing and speech reading. Brain Language, 64 (3), 269-281. https://doi.org/10.1006/brln.1998.1973
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1998). Impaired speech perception in poor readers: Evidence from hearing and speech reading. Brain Language, 64 (3), 269-281. https://doi.org/10.1006/brln.1998.1973
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1998). Impairment of speech-reading in prosopagnosia. Speech Communication, 26 (1-2), 89-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6393(98)00052-1
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1998). Impairment of speech-reading in prosopagnosia. Speech Communication, 26 (1-2), 89-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6393(98)00052-1
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & Bertelson, P. (1998). Upright but not inverted faces modify the perception of emotion in the voice. Cahiers de Psychologie Cognitive/Current Psychology of Cognition, 17 (4-5), 1021-1031.
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & Bertelson, P. (1998). Upright but not inverted faces modify the perception of emotion in the voice. Cahiers de Psychologie Cognitive/Current Psychology of Cognition, 17 (4-5), 1021-1031.
 Semenza, C., De Gelder, B., Piree, P., & Pizzi, M. (1998). Reading abilities in allographic agraphia.Brain and Language, 65 (1), 169-171.
Semenza, C., De Gelder, B., Piree, P., & Pizzi, M. (1998). Reading abilities in allographic agraphia.Brain and Language, 65 (1), 169-171.
 Vroomen, J., Tuomainen, J., & de Gelder, B. (1998). The roles of word stress and vowel harmony in speech segmentation. Journal of Memory and Language, 38 (2), 133-149. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmla.1997.2548
Vroomen, J., Tuomainen, J., & de Gelder, B. (1998). The roles of word stress and vowel harmony in speech segmentation. Journal of Memory and Language, 38 (2), 133-149. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmla.1997.2548
 Vroomen, J., van den Bosch, A., & de Gelder, B. (1998). A connectionist model for bootstrap learning of syllabic structure. Language and Cognitive Processes, 13 (2&3), 193-220. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/016909698386519
Vroomen, J., van den Bosch, A., & de Gelder, B. (1998). A connectionist model for bootstrap learning of syllabic structure. Language and Cognitive Processes, 13 (2&3), 193-220. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/016909698386519
Chapters
 Vroomen, J., Bosch, A. & de Gelder, B. (1998). A connectionist model for bootstrap learning of syllabic structure. In K. Plunkett (Ed.), Language acquisition and connectionism (pp. 193-220). Hove, U.K.: Psychology Press. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/016909698386519
Vroomen, J., Bosch, A. & de Gelder, B. (1998). A connectionist model for bootstrap learning of syllabic structure. In K. Plunkett (Ed.), Language acquisition and connectionism (pp. 193-220). Hove, U.K.: Psychology Press. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/016909698386519
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & Bachoud Levi, A. C. (1998). Impaired speechreading and audio-visual speech integration in prosopagnosia. In R. Campbell & B. Dodd (Eds.), Hearing by eye II: Advances in the psychology of speechreading and auditory visual speech (pp. 195-207). Hove, England: Psychology Press/Erlbaum (UK) Taylor & Francis.
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & Bachoud Levi, A. C. (1998). Impaired speechreading and audio-visual speech integration in prosopagnosia. In R. Campbell & B. Dodd (Eds.), Hearing by eye II: Advances in the psychology of speechreading and auditory visual speech (pp. 195-207). Hove, England: Psychology Press/Erlbaum (UK) Taylor & Francis.
1997
 Bertelson, P., de Gelder, B., & van Zon, M. (1997). Explicit speech segmentation and syllabic onset structure: Developmental trends. Psychological Research, 60 (3), 183-191. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00419766
Bertelson, P., de Gelder, B., & van Zon, M. (1997). Explicit speech segmentation and syllabic onset structure: Developmental trends. Psychological Research, 60 (3), 183-191. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00419766
 de Gelder, B., Teunisse, J.-P., & Benson, P. J. (1997). Categorical perception of facial expressions: Categories and their internal structure. Cognition and Emotion, 11 (1), 1-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/026999397380005
de Gelder, B., Teunisse, J.-P., & Benson, P. J. (1997). Categorical perception of facial expressions: Categories and their internal structure. Cognition and Emotion, 11 (1), 1-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/026999397380005
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1997). Modality effects in immediate recall of verbal and non-verbal information. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 9 (1), 97-110. https://doi.org/10.1080/713752541
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1997). Modality effects in immediate recall of verbal and non-verbal information. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 9 (1), 97-110. https://doi.org/10.1080/713752541
 Irausquin, R.S., & de Gelder, B. (1997). Serial recall of poor readers in two presentation modalities: Combined effects of phonological similarity and word length. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 65 (3), 342-369. https://doi.org/10.1006/jecp.1996.2361
Irausquin, R.S., & de Gelder, B. (1997). Serial recall of poor readers in two presentation modalities: Combined effects of phonological similarity and word length. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 65 (3), 342-369. https://doi.org/10.1006/jecp.1996.2361
 Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (1997). Activation of embedded words in spoken word recognition.Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 23 (3), 710-720. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0096-1523.23.3.710
Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (1997). Activation of embedded words in spoken word recognition.Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 23 (3), 710-720. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0096-1523.23.3.710
Chapters
 de Gelder, B., Etcoff, N., & Vroomen, J. (1997). Impairment of visual speech integration in prosopagnosia. Proceedings of the European Workshop on Audio-Visual speech Processing (pp. 77-80). Rhodos: European Workshop on Audio-Visual Speech Processing.
de Gelder, B., Etcoff, N., & Vroomen, J. (1997). Impairment of visual speech integration in prosopagnosia. Proceedings of the European Workshop on Audio-Visual speech Processing (pp. 77-80). Rhodos: European Workshop on Audio-Visual Speech Processing.
 Bertelson, P., Vroomen, J. & de Gelder, B. (1997). Auditory-visual interaction in voice localization and in bimodal speech recognition: The effects of desynchronization. Proceedings of the European Workshop on Audio-visual Speech Processing (pp. 97-100). Rhodos: European Workshop on Audio-visual Speech Processing.
Bertelson, P., Vroomen, J. & de Gelder, B. (1997). Auditory-visual interaction in voice localization and in bimodal speech recognition: The effects of desynchronization. Proceedings of the European Workshop on Audio-visual Speech Processing (pp. 97-100). Rhodos: European Workshop on Audio-visual Speech Processing.
 de Gelder, B., Etcoff, N. & Vroomen, J. (1997). Impairment of visual speech integration in prosopagnosia. Proceedings of the European Workshop on Audio-Visual speech Processing (pp. 77-80). Rhodos: European Workshop on Audio-Visual Speech Processing.
de Gelder, B., Etcoff, N. & Vroomen, J. (1997). Impairment of visual speech integration in prosopagnosia. Proceedings of the European Workshop on Audio-Visual speech Processing (pp. 77-80). Rhodos: European Workshop on Audio-Visual Speech Processing.
1996
 Campbell, R., de Gelder, B., & de Haan, E. (1996). The lateralization of lip-reading: A second look. Neuropsychologia, 34 (12), 1235-1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-3932(96)00046-2
Campbell, R., de Gelder, B., & de Haan, E. (1996). The lateralization of lip-reading: A second look. Neuropsychologia, 34 (12), 1235-1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-3932(96)00046-2
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1996). Auditory illusions as evidence for a role of the syllable in adult developmental dyslexics. Brain Language, 52 (2), 373-385. https://doi.org/10.1006/brln.1996.0018
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1996). Auditory illusions as evidence for a role of the syllable in adult developmental dyslexics. Brain Language, 52 (2), 373-385. https://doi.org/10.1006/brln.1996.0018
 Gepner, B., de Gelder, B., & de Schonen, S. (1996). Face processing in autistics: Evidence for a generalised deficit? Child Neuropsychology, 2 (2), 123-139. https://doi.org/10.1080/09297049608401357
Gepner, B., de Gelder, B., & de Schonen, S. (1996). Face processing in autistics: Evidence for a generalised deficit? Child Neuropsychology, 2 (2), 123-139. https://doi.org/10.1080/09297049608401357
 Vroomen, J., van Zon, M., & de Gelder, B. (1996). Cues to speech segmentation: Evidence from juncture misperceptions and word spotting. Memory and Cognition, 24 (6), 744-755. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03201099
Vroomen, J., van Zon, M., & de Gelder, B. (1996). Cues to speech segmentation: Evidence from juncture misperceptions and word spotting. Memory and Cognition, 24 (6), 744-755. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03201099
Chapters
 de Gelder, B., Bertelson, P. & Vroomen, J. (1996). Aspects of modality in audio-visual processes. In D.G. Stork & M.E. Hennecke (Eds.), Speechreading by humans and machines (pp. 179-192). Berlin: Springer Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-13015-5_13
de Gelder, B., Bertelson, P. & Vroomen, J. (1996). Aspects of modality in audio-visual processes. In D.G. Stork & M.E. Hennecke (Eds.), Speechreading by humans and machines (pp. 179-192). Berlin: Springer Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-13015-5_13
 de Gelder, B. (1996). Modularity and logical cognitivism. In A. Clark & P. Millican (Eds.),Connectionism, concepts and folk psychology (pp. 147-168). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
de Gelder, B. (1996). Modularity and logical cognitivism. In A. Clark & P. Millican (Eds.),Connectionism, concepts and folk psychology (pp. 147-168). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
1995
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Vanzon, M., & Popelier, T. (1995). Auditory misperceptions in adult developmental dyslexics. Brain and Cognition, 28 (1), 115-115.
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., Vanzon, M., & Popelier, T. (1995). Auditory misperceptions in adult developmental dyslexics. Brain and Cognition, 28 (1), 115-115.
 Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (1995). Metrical segmentation and lexical inhibition in spoken word recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 21 (1), 98-108. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0096-1523.21.1.98
Vroomen, J., & de Gelder, B. (1995). Metrical segmentation and lexical inhibition in spoken word recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 21 (1), 98-108. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0096-1523.21.1.98
Books
 de Gelder, B., & Morais, J. (1995). Speech and reading: A comparative approach. Oxford, England: Erlbaum (Uk) Taylor and Francis, Publ.
de Gelder, B., & Morais, J. (1995). Speech and reading: A comparative approach. Oxford, England: Erlbaum (Uk) Taylor and Francis, Publ.
Chapters
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1995). Memory deficits for heard and lip-read speech in young and adult poor readers. In B. de Gelder & J. Morais (Eds.), Speech and reading: A comparative approach (pp. 125 139). Oxford, England: Erlbaum (Uk) Taylor & Francis, Publ. xvi, 367 pp.
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1995). Memory deficits for heard and lip-read speech in young and adult poor readers. In B. de Gelder & J. Morais (Eds.), Speech and reading: A comparative approach (pp. 125 139). Oxford, England: Erlbaum (Uk) Taylor & Francis, Publ. xvi, 367 pp.
 de Gelder, B., & Morais, J. (1995). Introduction speech and reading: One side to two coins. In B. de Gelder & J. Morais (Eds.), Speech and reading: A comparative approach (pp. 1 13). Oxford, England: Erlbaum (Uk) Taylor & Francis, Publ. xvi, 367 pp.
de Gelder, B., & Morais, J. (1995). Introduction speech and reading: One side to two coins. In B. de Gelder & J. Morais (Eds.), Speech and reading: A comparative approach (pp. 1 13). Oxford, England: Erlbaum (Uk) Taylor & Francis, Publ. xvi, 367 pp.
1994
 de Gelder, B. (1994). The risks of rationalizing cognitive development. Behavioral and brain sciences, 17(4), 713-714.
de Gelder, B. (1994). The risks of rationalizing cognitive development. Behavioral and brain sciences, 17(4), 713-714.
 de Gelder, B., & van Baaren, R. (1994). Intentionalities: ToMM, SAM, EDD, ID, and the others.Cahiers de Psychologie Cognitive/Current Psychology of Cognition, 13 (5), 575-583.
de Gelder, B., & van Baaren, R. (1994). Intentionalities: ToMM, SAM, EDD, ID, and the others.Cahiers de Psychologie Cognitive/Current Psychology of Cognition, 13 (5), 575-583.
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1994). A new place for modality in a modular mind. Cahiers de Psychologie Cognitive/Current Psychology of Cognition, 13 (1), 84-91.
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1994). A new place for modality in a modular mind. Cahiers de Psychologie Cognitive/Current Psychology of Cognition, 13 (1), 84-91.
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1994). Memory for consonants versus vowels in heard and lipread speech. Journal of Memory and Language, 33 (6), 737-756. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmla.1994.1035
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1994). Memory for consonants versus vowels in heard and lipread speech. Journal of Memory and Language, 33 (6), 737-756. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmla.1994.1035
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1994). Metrical segmentation and lexical competition: A happy affair?Dokkyo International Review, 221-230.
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1994). Metrical segmentation and lexical competition: A happy affair?Dokkyo International Review, 221-230.
 Keatley, C. W., Spinks, J. A., & de Gelder, B. (1994). Asymmetrical cross-language priming effects. Memory and Cognition, 22 (1), 70-84. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03202763
Keatley, C. W., Spinks, J. A., & de Gelder, B. (1994). Asymmetrical cross-language priming effects. Memory and Cognition, 22 (1), 70-84. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03202763
 Teunisse, J. P., & de Gelder, B. (1994). Do autistics have a generalized face processing deficit?International Journal of Neuroscience, 77 (1-2), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207459408986014
Teunisse, J. P., & de Gelder, B. (1994). Do autistics have a generalized face processing deficit?International Journal of Neuroscience, 77 (1-2), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207459408986014
1993
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & Bertelson, P. (1993). The effects of alphabetic-reading competence on language representation in bilingual Chinese subjects. Psychology Research, 55 (4), 315-321. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00419691
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & Bertelson, P. (1993). The effects of alphabetic-reading competence on language representation in bilingual Chinese subjects. Psychology Research, 55 (4), 315-321. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00419691
1992
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1992). Abstract versus modality-specific memory representations in processing auditory and visual speech. Memory and Cognition, 20 (5), 533-538. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03199585
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1992). Abstract versus modality-specific memory representations in processing auditory and visual speech. Memory and Cognition, 20 (5), 533-538. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03199585
 Keatley, C., & de Gelder, B. (1992). The bilingual primed lexical decision task: Cross-language priming disappears with speeded responses. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 4 (4), 273-292. https://doi.org/10.1080/09541449208406188
Keatley, C., & de Gelder, B. (1992). The bilingual primed lexical decision task: Cross-language priming disappears with speeded responses. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 4 (4), 273-292. https://doi.org/10.1080/09541449208406188
Chapters
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1992). Auditory and visual speech perception in alphabetic and nonalphabetic Chinese-Dutch bilinguals. In R. J. Harris (Ed), Cognitive processing in bilinguals. Advances in psychology (pp. 413-426). Oxford, England: North Holland.
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1992). Auditory and visual speech perception in alphabetic and nonalphabetic Chinese-Dutch bilinguals. In R. J. Harris (Ed), Cognitive processing in bilinguals. Advances in psychology (pp. 413-426). Oxford, England: North Holland.
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1992). Auditory and visual speech perception in alphabetic and non-alphabetic Chinese-Dutch bilinguals. In J. Alegria, D. Holender, J. Morais & M. Radeau (Eds.),Cognitive processing in bilinguals (pp. 413-426). Amsterdam: Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4115(08)61508-3
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1992). Auditory and visual speech perception in alphabetic and non-alphabetic Chinese-Dutch bilinguals. In J. Alegria, D. Holender, J. Morais & M. Radeau (Eds.),Cognitive processing in bilinguals (pp. 413-426). Amsterdam: Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4115(08)61508-3
1991
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1991). Phonological deficits: Beneath the surface of reading acquisition problems. Psychological Research, 53 (1), 88-97. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00867336
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1991). Phonological deficits: Beneath the surface of reading acquisition problems. Psychological Research, 53 (1), 88-97. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00867336
 de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1991). Phonological deficits, a source of asymmetries between developmental and acquired dyslexia. Mind and Language, 6, 123-129.
de Gelder, B., & Vroomen, J. (1991). Phonological deficits, a source of asymmetries between developmental and acquired dyslexia. Mind and Language, 6, 123-129.
 de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & Van der Heide, L. (1991). Face recognition and lip-reading in autism. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 3 (1), 69-86. https://doi.org/10.1080/09541449108406220
de Gelder, B., Vroomen, J., & Van der Heide, L. (1991). Face recognition and lip-reading in autism. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 3 (1), 69-86. https://doi.org/10.1080/09541449108406220
Chapters
 de Gelder, B. (1991). Carnap, Fodor et le Cognitivisme Logique. In J.-N/ Missa (Ed.), Philosophie de l’Esprit et Sciences du Cerveau (pp. 123-133). Paris: Annales de l’Institut de Philosophie de l’Universite de Bruxelles.
de Gelder, B. (1991). Carnap, Fodor et le Cognitivisme Logique. In J.-N/ Missa (Ed.), Philosophie de l’Esprit et Sciences du Cerveau (pp. 123-133). Paris: Annales de l’Institut de Philosophie de l’Universite de Bruxelles.
 Bertelson, P., & de Gelder, B. (1991). The emergence of phonological awareness: Comparative approaches. In I.G. Mattingly & M. Studdert-Kennedy (Eds), Modularity and the motor theory of speech perception (pp. 393 412). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Bertelson, P., & de Gelder, B. (1991). The emergence of phonological awareness: Comparative approaches. In I.G. Mattingly & M. Studdert-Kennedy (Eds), Modularity and the motor theory of speech perception (pp. 393 412). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
 de Gelder, B., (1991). Intentional ascription, autism and troubles with content. In J. Verschueren (Ed.). Pragmatics at issue (pp. 171-191). Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
de Gelder, B., (1991). Intentional ascription, autism and troubles with content. In J. Verschueren (Ed.). Pragmatics at issue (pp. 171-191). Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
1990 and earlier
 de Gelder, B. (1990). The matter of other minds. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 13 (3), 582-584. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X00080262
de Gelder, B. (1990). The matter of other minds. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 13 (3), 582-584. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X00080262
 de Gelder, B. (1987). On not having a theory of mind. Cognition, 27(3), 285-290. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1016/S0010-0277(87)80013-6
de Gelder, B. (1987). On not having a theory of mind. Cognition, 27(3), 285-290. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1016/S0010-0277(87)80013-6
Chapters
 de Gelder, B. (1990). Phonological awareness, misidentification and multiple identities. In J.A. Admonson, P. Muelhauser & C. Feagin (Eds.). Development and diversity: Linguistic variation across time and space (pp. 483-505). Berlin: Springer.
de Gelder, B. (1990). Phonological awareness, misidentification and multiple identities. In J.A. Admonson, P. Muelhauser & C. Feagin (Eds.). Development and diversity: Linguistic variation across time and space (pp. 483-505). Berlin: Springer.